
NVIDIA’s New Accelerated Computing Libraries: A Game Changer in Speed and Energy Efficiency
Overview
NVIDIA, a leader in GPU-accelerated computing, has unveiled a suite of new libraries designed to deliver significant speed boosts and reduce energy consumption across various computing tasks. These libraries span applications in data processing, generative AI, recommender systems, AI data curation, 6G research, AI-physics, and more. The innovations include:
- LLM Applications: NeMo Curator for custom dataset creation and Nemotron-4 340B for high-quality synthetic data generation.
- Data Processing: cuVS for rapid vector search and a new Polars GPU Engine in open beta.
- Physical AI: Warp for physics simulation, Aerial for wireless network simulation, and Sionna for link-level wireless simulation with real-time inference capabilities.
These advancements have enabled companies worldwide to significantly accelerate applications previously limited to CPU processing, resulting in extreme speedups and impressive energy savings.
Real-World Applications and Impact
Industrial Simulations
In Houston, CPFD, a company specializing in computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation software for industrial applications, has leveraged NVIDIA’s accelerated computing to great effect. Their Barracuda Virtual Reactor software, used in designing next-generation recycling facilities, now runs efficiently on cloud instances powered by NVIDIA GPUs. This shift allows plastic recycling facilities to scale their simulations 400 times faster and 140 times more energy-efficiently than traditional CPU-based workstations.

Bottles being loaded into a plastics recycling facility. AI-generated image.
Video Conferencing
A widely-used video conferencing application, responsible for captioning hundreds of thousands of virtual meetings per hour, has also benefited from GPU acceleration. Initially, the application could query a transformer-powered speech recognition AI model three times a second using CPUs. After transitioning to GPUs in the cloud, the throughput soared to 200 queries per second, achieving a 66x speedup and a 25x improvement in energy efficiency.
E-commerce
An e-commerce website connecting millions of shoppers daily has also experienced significant improvements by adopting NVIDIA’s accelerated computing. Their advanced recommendation system, powered by a deep learning model, saw a 33x speedup and nearly 12x energy-efficiency improvement after switching from CPUs to GPUs in the cloud.
The Future of Accelerated Computing
With the exponential growth of data, accelerated computing in the cloud is poised to enable even more innovative use cases. NVIDIA estimates that if all AI, high-performance computing (HPC), and data analytics workloads currently running on CPU servers were instead GPU-accelerated, data centers could save 40 terawatt-hours of energy annually—equivalent to the energy consumption of 5 million U.S. homes per year.
Sustainable Computing with CUDA GPUs
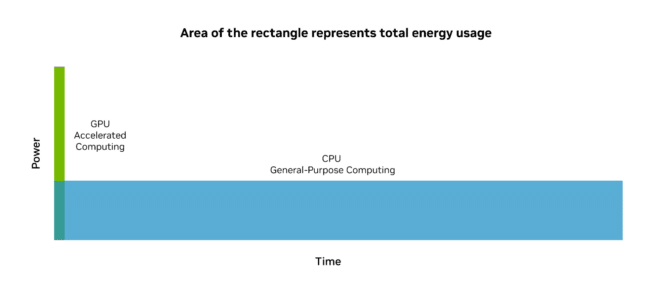
Accelerated computing leverages the parallel processing capabilities of CUDA GPUs to perform tasks orders of magnitude faster than CPUs, thereby boosting productivity while dramatically reducing cost and energy consumption. Although adding GPUs increases the peak power of a CPU-only server, the overall energy consumption is significantly lower due to the GPUs’ ability to complete tasks quickly and enter a low-power state.

GPUs achieve 20x greater energy efficiency compared to traditional computing on CPU-only servers.
Over the past decade, NVIDIA AI computing has achieved approximately 100,000 times more energy efficiency in processing large language models (LLMs). To illustrate, if cars had improved in efficiency as much as NVIDIA’s AI platform, they would get 500,000 miles per gallon—enough to drive to the moon and back on less than a gallon of gasoline.
Performance Boosts Across Various Workloads
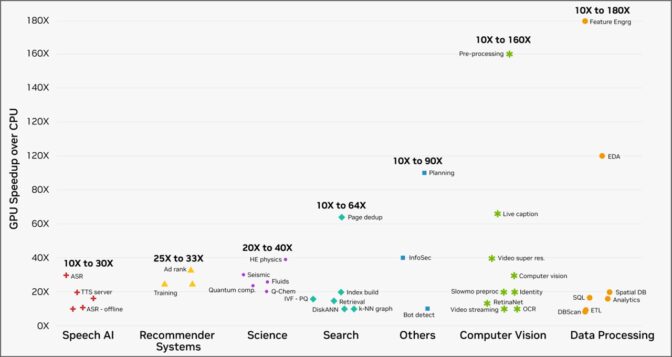
Using NVIDIA’s accelerated computing platform, customers running workloads on cloud service providers have observed speedups of 10 to 180 times across various real-world tasks, from data processing to computer vision.

Speedups of 10-180x achieved in real-world implementations by cloud customers across workloads with the NVIDIA accelerated computing platform.
Addressing Compute Inflation
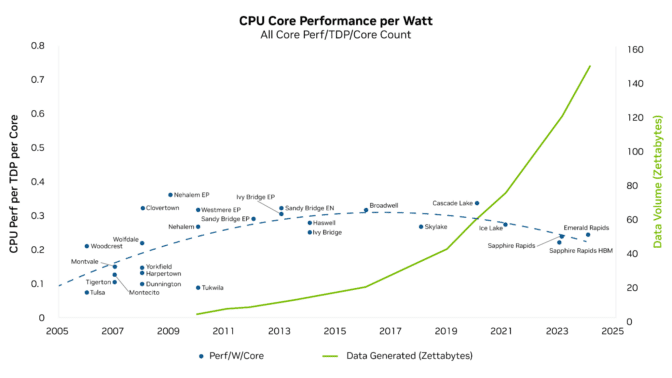
As data growth continues to outpace the growth in compute performance per watt of CPUs, a phenomenon known as "compute inflation" has emerged. This growing performance gap underscores the importance of GPU acceleration in meeting the increasing demand for computing power.

The widening gap between data growth and the lagging compute performance per watt of CPUs.
Specialized Libraries for Diverse Applications
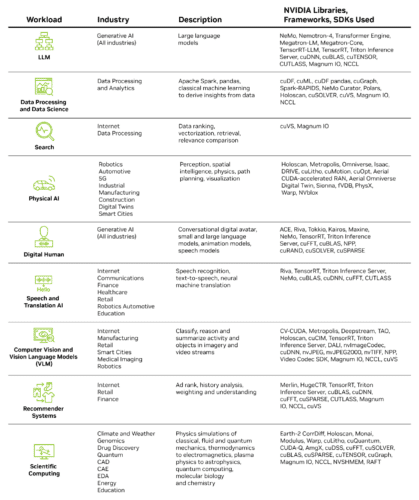
NVIDIA offers a wide array of specialized CUDA libraries to accelerate specific workloads. These libraries, optimized to harness the hardware features of NVIDIA GPUs, cover diverse use cases:
LLM Applications
- NeMo Curator: Enables developers to quickly create custom datasets for large language model use cases, now with multimodal support including image curation.
- Nemotron-4 340B: A new suite of models for synthetic data generation, allowing businesses to build custom models.
Data Processing Applications
- cuVS: An open-source library for GPU-accelerated vector search and clustering, enabling large indexes to be built in minutes.
- Polars: An open-source library for efficient data processing, now with a GPU engine powered by NVIDIA’s cuDF library, offering up to a 10x performance boost.
Physical AI
- Warp: Accelerates physics simulation and graphics, with a new Tile API for matrix and Fourier computations.
- Aerial: Includes platforms for designing, simulating, and operating wireless networks, now with more map formats for ray tracing and higher accuracy simulations.
- Sionna: A library for link-level simulations of wireless and optical communication systems, now with a toolchain for real-time inference using NVIDIA TensorRT.
NVIDIA provides over 400 libraries, including CV-CUDA for computer vision tasks, and cuDF for accelerating data frames and tables central to SQL databases and pandas in data science.

CAD – Computer-Aided Design, CAE – Computer-Aided Engineering, EDA – Electronic Design Automation.
For researchers who prefer not to build their own pipelines, NVIDIA NIM offers a streamlined path to production deployment by packaging multiple libraries and AI models into optimized containers.
Hardware-Based Acceleration Features
NVIDIA’s hardware platforms, such as the Blackwell platform, include features like a decompression engine that unpacks compressed data files up to 18 times faster than CPUs. This significantly accelerates data processing applications that frequently access compressed files.
Conclusion
The integration of NVIDIA’s specialized CUDA GPU-accelerated libraries into cloud computing platforms offers remarkable speed and energy efficiency across a variety of workloads. This not only drives significant cost savings for businesses but also contributes to sustainable computing, benefiting billions of users who rely on cloud-based workloads.
To learn more about NVIDIA’s sustainable computing efforts, visit NVIDIA’s sustainable computing page and explore the Energy Efficiency Calculator to discover potential energy and emissions savings.


































