The NISAR Mission: A New Era in Earth Observation
In a significant advancement for Earth observation, the upcoming NISAR mission, a collaboration between the United States and India, is set to redefine how we monitor our planet’s dynamic surface. The NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) satellite is poised to deliver unprecedented insights into Earth’s evolution and the impacts of natural phenomena and human activities.
An Overview of NISAR
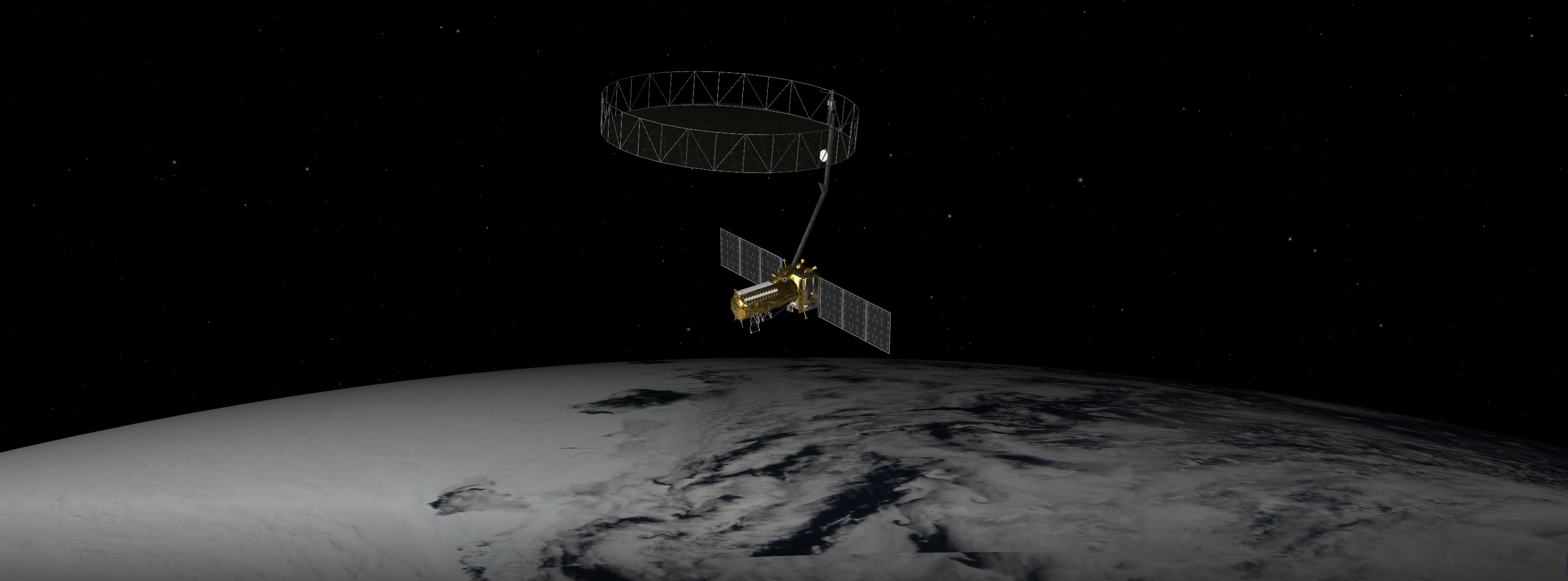
The NISAR mission is a groundbreaking initiative featuring a dual-band radar satellite that aims to observe and measure the Earth’s surface with unmatched precision. It is particularly focused on detecting land deformations resulting from natural events such as earthquakes, landslides, and volcanic activities. Moreover, NISAR will monitor the movement of glaciers and ice sheets, offering critical data on these frozen regions’ expansion or contraction. Additionally, the satellite will track changes in forests and wetlands, which are vital for understanding the global carbon cycle.
The Journey to Launch
The path to launching NISAR has been as remarkable as the mission itself. Scheduled for launch in the near future, the project has seen extensive development and collaboration across continents. Paul Rosen, the project scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California, has been instrumental in guiding the mission from conception to its impending launch.
Capturing Earth’s Changes
Earth is in a constant state of flux, experiencing both subtle and dramatic changes. NISAR will capture these transformations with remarkable detail, offering a comprehensive view of the planet’s land and ice surfaces. The satellite will provide weekly updates, with each image pixel representing an area approximately half the size of a tennis court. This frequency and level of detail will enable scientists to construct a coherent narrative of Earth as a dynamic and interconnected system.
Advanced Radar Technology
NISAR is set to become the first Earth-observing satellite to be equipped with two distinct radar systems: an L-band radar with a 10-inch wavelength and an S-band radar with a 4-inch wavelength. The difference in wavelengths allows for varied interaction with the Earth’s surface. Shorter wavelengths, like those of the S-band, are more responsive to smaller objects such as leaves and rough surfaces, while the longer L-band wavelengths interact more with larger objects such as rocks and tree trunks. The dual-band capability allows researchers to study a broader array of features by analyzing how each radar band interacts with different elements on Earth.
Historical Context and Technological Evolution
The concept of using spaceborne synthetic aperture radar (SAR) to study Earth’s processes dates back to the 1970s with NASA’s Seasat mission. Although Seasat operated only for a short period, it produced pioneering images that transformed the field of remote sensing. This mission was a precursor to further developments like the Shuttle Imaging Radar program and the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission.
Data Accessibility and Applications
NISAR’s data products are designed to serve a wide range of scientific needs. The mission focuses on ecosystems, the cryosphere (Earth’s frozen areas), and the solid Earth, but its applications extend beyond basic research. For example, it will be useful in monitoring soil moisture and water resources. To accommodate the vast amount of data generated, NASA has opted to process and store it in the cloud, ensuring free and easy access for users worldwide.
Collaboration and Development
The idea for NISAR emerged from the 2007 Decadal Survey by the National Academy of Sciences, which proposed the DESDynI (Deformation, Ecosystem Structure, and Dynamics of Ice) mission. Around the same time, ISRO was considering an S-band satellite. The two organizations decided to collaborate, and in 2014, they formalized their partnership, marking the beginning of a unique dual-band mission.
The collaboration between NASA and ISRO spans over 9,000 miles and encompasses 13 time zones. The satellite’s components were manufactured on different continents and later assembled in India. This extensive partnership underscores the mission’s global significance and the challenges overcome to bring it to fruition.
Contributions from NASA and ISRO
The NISAR mission is a testament to equal collaboration between NASA and ISRO. Managed by Caltech, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) oversees the U.S. elements of the mission, including the L-band SAR. NASA is also responsible for providing the radar reflector antenna, the deployable boom, a communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder, and a payload data subsystem.
On the Indian side, the Space Applications Centre in Ahmedabad leads the development of the S-band SAR instrument and handles its calibration, data processing, and the creation of scientific algorithms. The U R Rao Satellite Centre in Bengaluru is responsible for the spacecraft bus. The launch vehicle comes from ISRO’s Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre, with launch services managed by ISRO’s Satish Dhawan Space Centre. The satellite’s mission operations are conducted by ISRO’s Telemetry Tracking and Command Network, while the National Remote Sensing Centre in Hyderabad manages S-band data reception, operational product generation, and dissemination.
A Unique Window on Earth
NISAR’s dual-band radar technology and international collaboration make it a unique tool for observing Earth. Its ability to provide detailed, frequent updates on a wide range of Earth’s features will enhance our understanding of natural processes and inform responses to natural disasters. The mission is set to pave the way for future Earth observation initiatives, demonstrating the potential of international cooperation in advancing scientific knowledge.
For more detailed information about the NISAR mission, you can visit the official website at NISAR.
For more Information, Refer to this article.