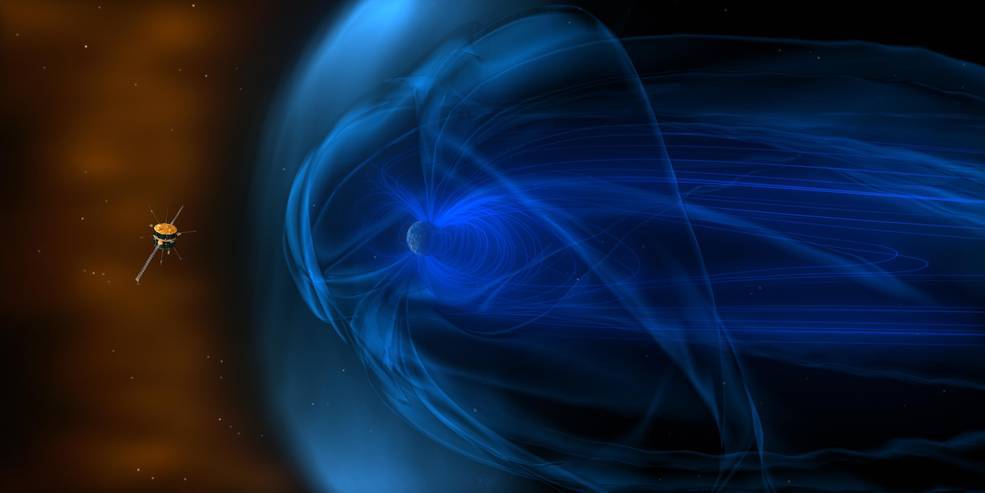
NASA’s Wind Spacecraft: A Long-Lasting Beacon in Space
The Wind spacecraft, a vital component of NASA’s scientific fleet, continues to deliver valuable data about solar wind and its effects on Earth, even decades after its launch. Originally sent into space in 1994, Wind was designed to study solar wind—streams of charged particles emitted by the Sun—and its interactions with the Earth’s magnetic field. This mission has been integral in providing insights into solar phenomena and space weather, which can impact satellite communications and power grids on Earth.
Wind’s Endurance and Fuel Reserves
According to Lynn Wilson, the Wind project scientist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, the spacecraft’s longevity is not solely determined by its fuel reserves. "Based on fuel alone, Wind can continue flying until 2074," Wilson noted. This means that, in terms of fuel, the spacecraft has the capacity to remain operational for another five decades. However, the spacecraft’s ability to continue sending data back to Earth is contingent upon the functionality of its last surviving digital tape recorder.
The Crucial Role of the Digital Tape Recorder
The digital tape recorder onboard Wind is a critical component for data storage and transmission. In the early days of the mission, this technology was state-of-the-art, capable of recording large volumes of data before sending it back to Earth. As the spacecraft travels through space, it encounters various environmental challenges that can degrade its systems. The tape recorder’s durability and performance are key factors that will ultimately determine how much longer Wind can continue to contribute to scientific research.
Importance of Wind’s Data
Wind’s data has been crucial in understanding the dynamics of the solar wind and its interaction with the Earth’s magnetosphere. The magnetosphere is a region around Earth dominated by the planet’s magnetic field, which protects us from harmful solar and cosmic radiation. By studying solar wind, scientists can better predict space weather phenomena, such as geomagnetic storms, which can have significant effects on satellite operations, GPS systems, and even power grids.
The Impact of Space Weather
Space weather refers to the environmental conditions in space as influenced by the Sun and the solar wind. When solar wind reaches the Earth, it can cause disturbances in the magnetosphere, leading to phenomena such as auroras (Northern and Southern Lights) and geomagnetic storms. These storms can disrupt satellite communications, affect navigation systems, and even cause power outages by inducing currents in power lines. Understanding space weather is essential for maintaining the reliability of technological systems that modern society depends on.
The Future of Space Weather Research
As Wind continues to operate, it remains a valuable asset for scientists studying space weather. Its data helps researchers develop models and forecasts that can predict when solar storms might occur and how severe they might be. This information is crucial for preparing and protecting infrastructure on Earth, minimizing the potential impacts of space weather events.
The Legacy of the Wind Spacecraft
Wind has surpassed its expected lifespan and continues to provide critical data, thanks to the robust engineering and design implemented by NASA. Its resilience is a testament to the ingenuity of the scientists and engineers who developed and launched the mission. The spacecraft’s ongoing contributions to space weather research highlight the importance of investing in long-term scientific missions, which can yield valuable insights for decades.
Conclusion
The Wind spacecraft remains an enduring testament to NASA’s commitment to exploring and understanding the space environment. While its fuel reserves suggest it could continue to operate until 2074, the ultimate determinant of its lifespan will be the digital tape recorder’s functionality. As Wind continues to gather and transmit data, it plays a crucial role in advancing our knowledge of space weather and its effects on Earth. The lessons learned from Wind’s mission continue to inform future space exploration and research, underscoring the importance of long-term scientific investment.
For those interested in learning more about the Wind spacecraft and its mission, further information is available on NASA’s official website.
For more Information, Refer to this article.