The Hubble Space Telescope: A Celestial Marvel
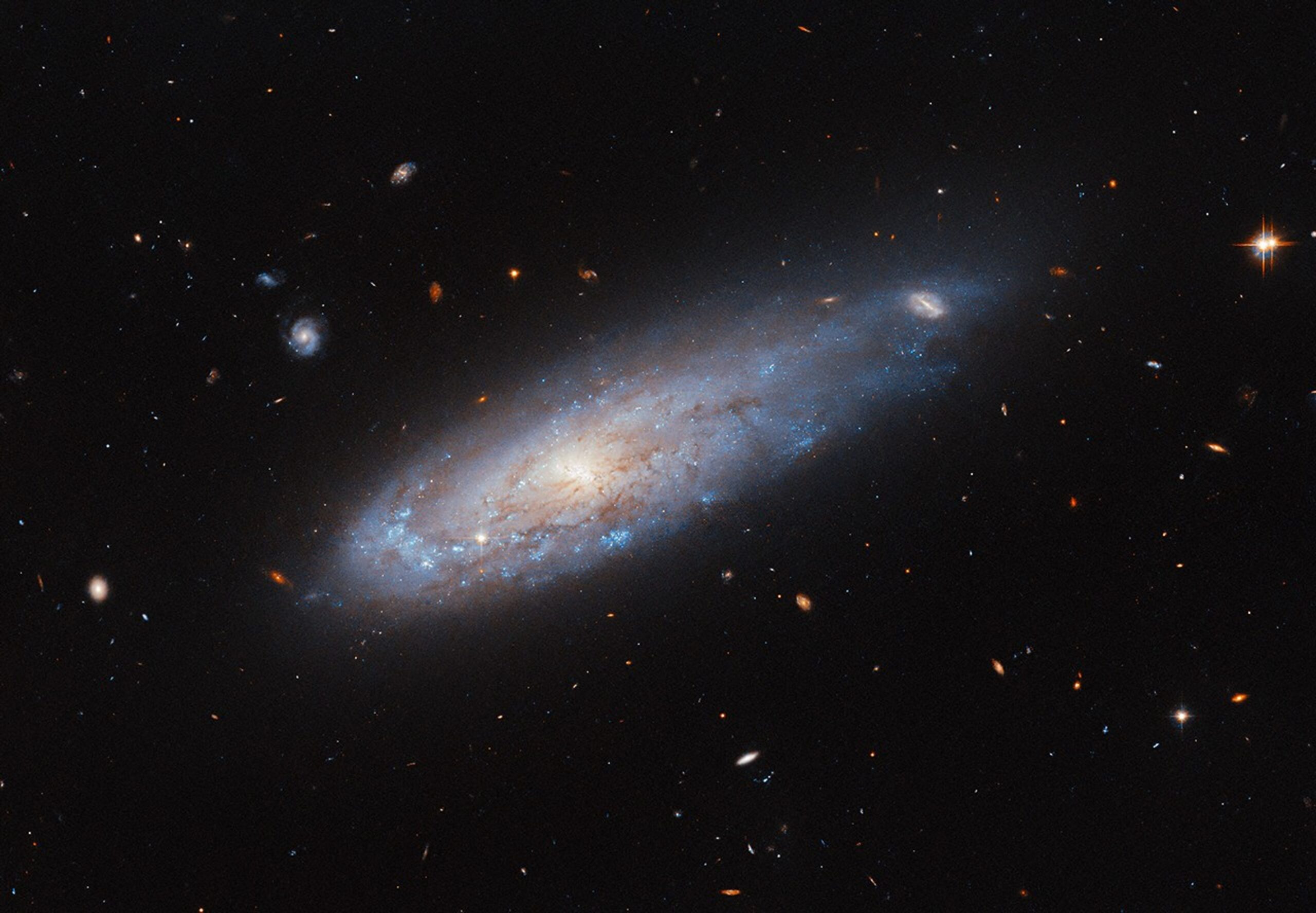
The Hubble Space Telescope, an essential tool in the arsenal of modern astronomy, continues to provide us with breathtaking insights into the universe. Recently, it captured an extraordinary image of the spiral galaxy IC 3225. This celestial body, located about 100 million light-years from Earth, visually resembles a cannonball racing through space, leaving behind a trail of gas akin to a comet’s tail. The imagery and data sent back by Hubble offer not just stunning visuals but also a deeper understanding of the dynamic processes occurring in galaxies far beyond our own Milky Way.
An Intriguing View of IC 3225
The recent image of IC 3225 captured by Hubble presents a galaxy that appears to be in motion, almost as if it were launched from a cosmic cannon. This impression is due to the galaxy’s structure and the effects of its environment. The galaxy seems compressed on one side, with a dense concentration of bright blue spots indicating active star formation. These blue regions are filled with newly formed, hot stars that illuminate the galaxy’s spiral arm, which curls around its disk. Conversely, the opposite end of the galaxy stretches into a short tail, seemingly distorted by the gravitational forces at play in its surroundings.
IC 3225 resides within the Virgo Cluster, a massive conglomeration of over 1,300 galaxies. This cluster is one of the densest known, and its gravitational influence is immense. The space between the galaxies in this cluster is filled with hot gas, known as the intracluster medium. As galaxies like IC 3225 navigate through this medium, they encounter what is termed as ‘ram pressure.’ This force is akin to the resistance experienced when moving through a thick fluid. The ram pressure exerted by the intracluster medium can strip a galaxy of its star-forming gas and dust, altering its structure and star formation activity.
The Role of Ram Pressure
Ram pressure stripping is a phenomenon crucial to understanding the evolution of galaxies in dense environments like the Virgo Cluster. As IC 3225 speeds through the intracluster medium, this pressure acts against its motion, effectively stripping away gas and dust from the galaxy. This process can significantly reduce or even halt star formation, as these stripped materials are essential for birthing new stars. However, the same pressure can also compress regions of the galaxy, triggering bursts of star formation.
For IC 3225, evidence suggests it has experienced ram pressure stripping in the past. The galaxy’s asymmetrical shape, with a compressed side showing more star formation activity, indicates the impact of these cosmic forces. While the galaxy is not currently near the cluster’s core, where such effects are most pronounced, its past interactions have left a lasting imprint on its structure.
The Dynamic Environment of the Virgo Cluster
The Virgo Cluster, where IC 3225 is located, is a vibrant and active region of the universe. This cluster is not just a collection of galaxies but a dynamic system with galaxies moving in fast orbits around its center. The gravitational interactions between these galaxies can lead to close encounters, further distorting their shapes and altering their trajectories.
The high density of the Virgo Cluster means that galaxies frequently interact with one another and the intracluster medium. These interactions can result in spectacular displays of gravitational forces at work, as seen with IC 3225. Such environments provide astronomers with the opportunity to study the effects of galaxy interactions and the role of the intracluster medium in shaping galaxy evolution.
Hubble’s Legacy and Ongoing Impact
Since its launch in 1990, the Hubble Space Telescope has been a cornerstone in advancing our understanding of the universe. It has provided a wealth of data, allowing scientists to explore phenomena such as the lifecycle of stars, the formation of galaxies, and the expansion of the universe. Hubble’s ability to capture detailed images of distant galaxies like IC 3225 continues to be a testament to its enduring value to the scientific community.
The telescope’s observations have not only expanded our knowledge but have also inspired countless individuals by bringing the wonders of the universe to the public eye. The images and discoveries made by Hubble have a profound cultural impact, sparking curiosity and a deeper appreciation for the cosmos.
The Future of Space Observation
While Hubble remains operational, the field of space observation is evolving with new technologies and missions. The upcoming James Webb Space Telescope, for example, is set to complement and expand on Hubble’s discoveries. With its advanced capabilities, Webb will explore different wavelengths of light and delve deeper into the early universe, offering insights into the origins of stars and galaxies.
These advancements in space observation technology promise to continue the legacy of discovery and innovation that Hubble has established. As we look to the future, the collaboration between telescopes like Hubble and Webb will undoubtedly unlock new mysteries and broaden our understanding of the universe.
Conclusion
The Hubble Space Telescope’s recent capture of the spiral galaxy IC 3225 is a vivid reminder of the dynamic and ever-changing nature of the universe. Through its observations, we gain not only a visual appreciation of distant galaxies but also a deeper understanding of the forces shaping them. As Hubble continues to operate and new telescopes join the field, the future of astronomical exploration holds exciting potential for uncovering the secrets of the cosmos.
For more detailed information and to view the awe-inspiring images captured by Hubble, you can visit the official NASA Science website here.
This ongoing journey of discovery through the Hubble Space Telescope and its successors promises to enrich our knowledge and inspire future generations to explore the vast unknowns of space.
For more Information, Refer to this article.