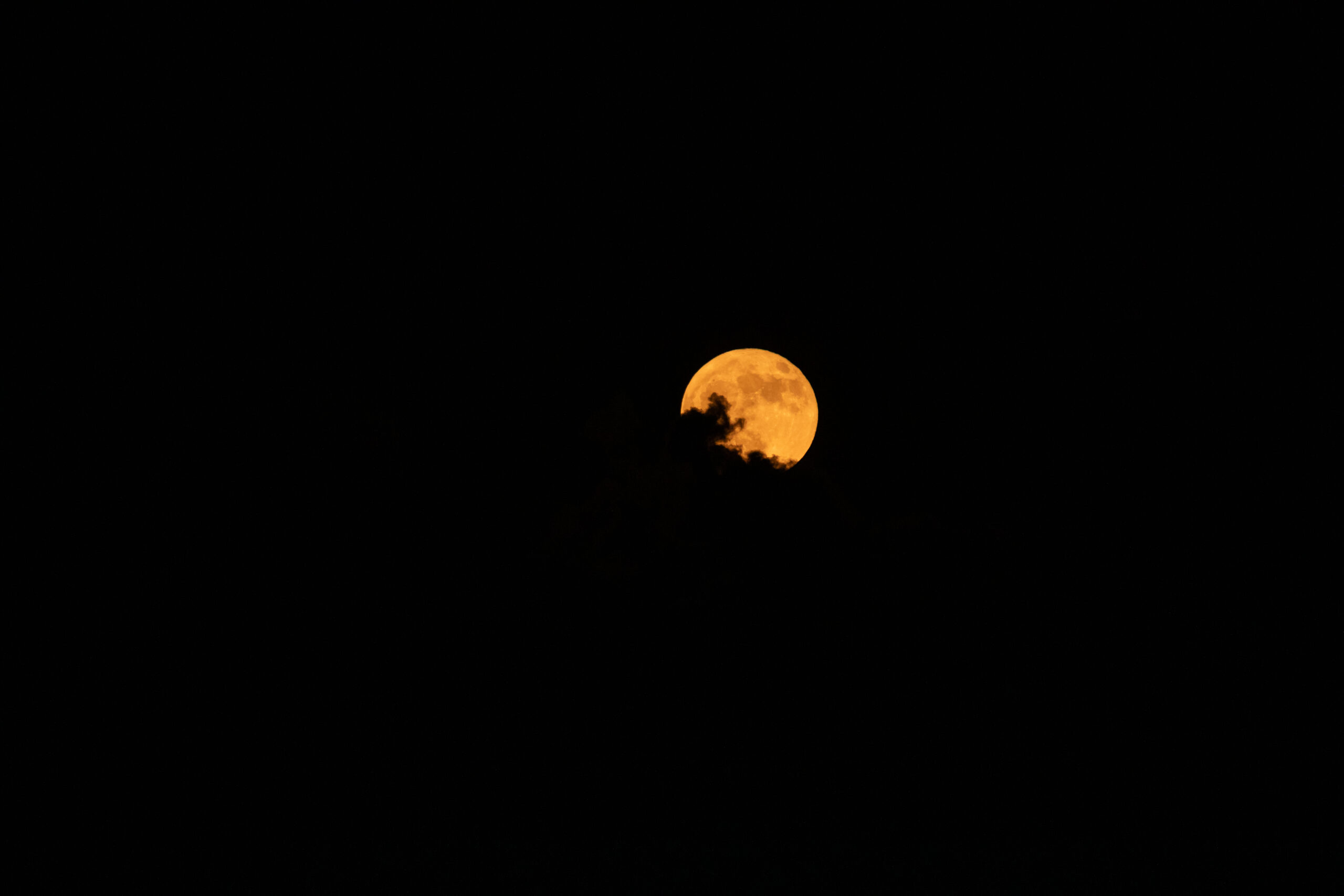
Eerie Beauty of the Blue Moon
On the evening of August 19, 2024, the night sky presented an enchanting yet mysterious spectacle as clouds wrapped around the full "blue" moon. Contrary to what the name might suggest, a blue moon is not actually blue in color. This term refers to a unique occurrence in the lunar calendar. Typically, a season has three full moons, but when a fourth full moon appears within the same season, the third is termed a "blue" moon. This rare event adds a touch of intrigue to the celestial sphere, captivating skywatchers and astronomy enthusiasts alike.
Upcoming Celestial Event: Europa in View
As we turn our gaze forward to the early morning hours of October 25, another fascinating celestial body will make its appearance in the sky. Jupiter’s icy moon, Europa, will be visible near Jupiter. This moon, known for its smooth, ice-covered surface, has become a point of interest for scientists and astronomers due to its potential to harbor life beneath its frozen crust. The moon will be easily observable with the aid of binoculars, appearing distinctively on one side of the gas giant, Jupiter.
Europa is not just any moon; it is a significant focus of NASA’s recent explorations. The space agency has launched a mission named the Europa Clipper, specifically aimed at studying this intriguing satellite. The mission’s goal is to gather more data about Europa’s surface and subsurface ocean, which could potentially support life. Observing Europa during this time offers a unique opportunity for those interested in the mysteries of our solar system.
Understanding Europa and the Europa Clipper Mission
Europa is one of Jupiter’s largest moons and is primarily composed of silicate rock with a water-ice crust. Beneath this icy exterior lies a vast ocean, which is more than twice the volume of all of Earth’s oceans combined. This ocean, coupled with the moon’s geologically active surface, makes Europa one of the most promising places to search for extraterrestrial life within our solar system.
The Europa Clipper mission is designed to conduct detailed reconnaissance of Europa’s ice shell and subsurface ocean. By doing so, NASA hopes to uncover the mysteries of this moon’s potential habitability. The mission will employ a suite of scientific instruments to study the composition and physical characteristics of Europa’s surface and subsurface, as well as its magnetic field and atmosphere.
Skywatching Tips for Observing Europa
For those interested in observing Europa and Jupiter, here are some tips to enhance your skywatching experience:
- Timing: The best time to observe Europa will be in the early morning hours of October 25. Make sure to check your local time for optimal viewing conditions.
- Equipment: While Europa can be seen with the naked eye, using binoculars or a small telescope will provide a clearer view. Binoculars will help you distinguish Europa as a bright spot near Jupiter.
- Location: Find a location away from city lights to reduce light pollution. A dark, elevated spot will provide the best viewing conditions.
- Weather: Clear skies are essential for a good observation. Check the weather forecast and look for nights with minimal cloud cover.
The Fascination with Jupiter’s Moons
Jupiter, the largest planet in our solar system, is accompanied by a multitude of moons, each with its own unique characteristics. Among these, Europa stands out due to its potential for life, but other moons like Ganymede and Callisto also offer intriguing features worthy of study.
Ganymede, the largest moon in the solar system, is larger than the planet Mercury and is known for its magnetic field. Callisto, on the other hand, is heavily cratered, suggesting an ancient and relatively unchanged surface. These moons, along with Europa, form a captivating part of Jupiter’s celestial entourage and continue to be subjects of scientific exploration and discovery.
Why Studying Europa Matters
The study of Europa goes beyond the search for extraterrestrial life; it also provides insights into the fundamental processes that shape planetary bodies. Understanding Europa’s geology, ocean, and ice dynamics can offer clues about similar processes on Earth and other icy worlds. This knowledge not only satisfies human curiosity but also aids in the planning of future space missions aimed at exploring other parts of our solar system.
Reactions and Reviews from the Scientific Community
The scientific community has shown great enthusiasm for the Europa Clipper mission. Researchers and astronomers worldwide are eager to analyze data collected by the mission’s instruments, which could revolutionize our understanding of icy moons and their potential to support life. The mission is seen as a stepping stone for future explorations, possibly paving the way for more ambitious endeavors, such as landing missions or even missions to drill through Europa’s ice to directly explore its ocean.
Conclusion
The upcoming opportunity to observe Europa alongside Jupiter presents a marvelous chance to witness one of the solar system’s most intriguing moons. As scientific missions like the Europa Clipper progress, our comprehension of these distant worlds continues to expand, enriching our understanding of the universe and our place within it.
For those interested in keeping up with such celestial events and missions, NASA’s website provides a wealth of information and skywatching tips to make the most of these astronomical phenomena. By staying informed and engaged, we can all partake in the wonders of the cosmos, fueling our imaginations and scientific endeavors alike.
For further information and tips on skywatching, you can visit NASA’s skywatching guide here.
For more Information, Refer to this article.