NASA’s Comprehensive Analysis of Hurricane Helene
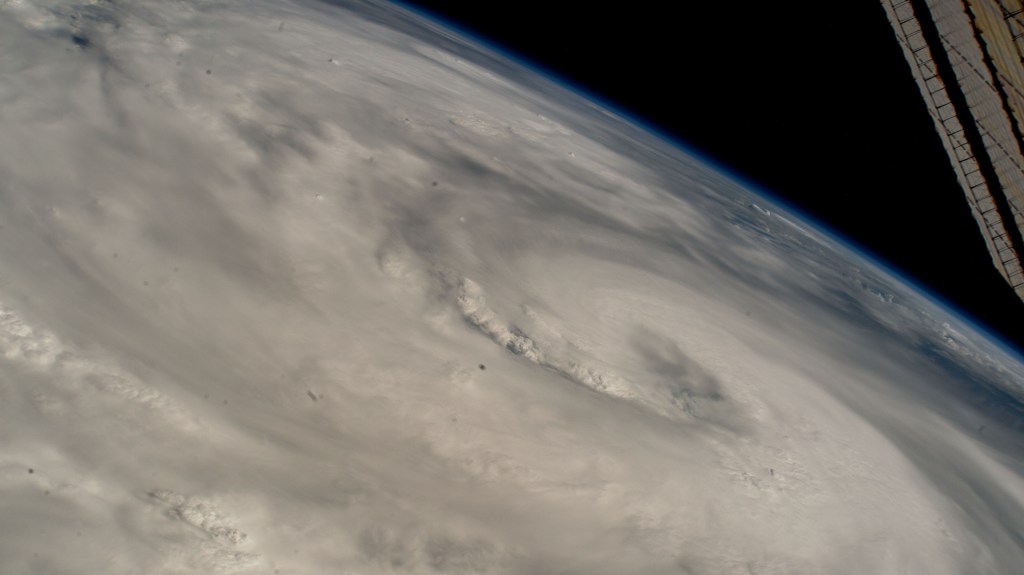
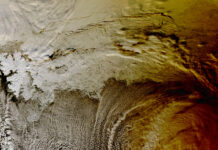
In recent observations, NASA has been actively monitoring Hurricane Helene as it made its way over the Gulf of Mexico. Captured from the International Space Station (ISS) while orbiting 257 miles above the Earth, a stunning image of the hurricane provides invaluable data for researchers. This image not only showcases the sheer magnitude of Helene but also underscores NASA’s commitment to studying severe weather phenomena from a unique vantage point.
Hurricane Helene stands as a testament to the power of nature, with its swirling clouds and intense energy captured in striking detail. The ISS, a collaborative effort among space agencies across the globe, serves as an essential platform for scientists to observe and analyze atmospheric conditions from space. By observing hurricanes like Helene, scientists can better understand their formation, evolution, and potential impact on populated regions.
This endeavor is part of NASA’s broader mission to enhance our understanding of Earth’s complex climate systems. Through satellite imagery and data collected from space, researchers can refine predictive models, thereby improving the accuracy of weather forecasts. This information is crucial for governments and agencies tasked with preparing for and responding to natural disasters, ultimately saving lives and reducing economic losses.
New Discoveries in Storm Clouds: Gamma-ray Emission Unveiled by NASA
In a groundbreaking study, NASA scientists have discovered a new type of gamma-ray emission within storm clouds, thanks to observations made from a NASA research aircraft. Gamma rays, which are high-energy electromagnetic waves, are typically associated with cosmic phenomena. However, their detection within Earth’s storm clouds opens up a new frontier in atmospheric science.
The discovery was made possible through advanced instrumentation aboard a NASA aircraft dedicated to studying atmospheric phenomena. These instruments can detect electromagnetic emissions far beyond the visible spectrum, enabling scientists to observe phenomena that are otherwise hidden from the naked eye. The ability to capture gamma-ray emissions in storm clouds offers a deeper understanding of the electrical processes occurring within these weather systems.
Gamma rays are produced when energetic particles are accelerated by electric fields within thunderstorms. This phenomenon, known as terrestrial gamma-ray flashes (TGFs), occurs in the upper regions of thunderstorm clouds. These emissions are of particular interest because they represent the most energetic natural phenomena on Earth, rivaling those observed in space.
This discovery has significant implications for our understanding of thunderstorms and their role in Earth’s climate system. By studying TGFs, scientists can gain insights into the electrical properties of storms, which could advance our knowledge of how these systems develop and evolve. Additionally, understanding gamma-ray emissions from thunderstorms may have implications for aviation safety, as aircraft frequently encounter these weather systems during flight.
NASA’s Instruments Capture the Sharpest Image of Earth’s Radiation Belt
NASA has achieved a remarkable milestone by capturing the most detailed image of Earth’s radiation belts, also known as the Van Allen belts. These belts, composed of charged particles trapped by Earth’s magnetic field, play a critical role in protecting our planet from harmful solar and cosmic radiation.
The Van Allen belts were first discovered in 1958 and have been the subject of extensive study ever since. They consist of two main layers, the inner and outer belts, which are filled with high-energy particles originating from the solar wind and cosmic rays. The belts act as a protective shield, absorbing and deflecting these particles, thereby safeguarding Earth’s atmosphere and surface.
NASA’s latest achievement in imaging these belts was made possible by cutting-edge instruments aboard the Van Allen Probes, a pair of spacecraft launched in 2012. These instruments are designed to measure the energy, angle, and composition of particles within the belts, providing unprecedented insights into their behavior and characteristics.
The new images reveal the dynamic nature of the radiation belts, which are influenced by solar activity and geomagnetic storms. By studying these belts in greater detail, scientists can better understand their variability and how they interact with space weather events. This knowledge is crucial for protecting satellites and other spacecraft operating in or near the belts, as well as for ensuring the safety of astronauts on missions beyond low Earth orbit.
The study of Earth’s radiation belts also has broader implications for understanding similar phenomena around other planets in our solar system. By comparing the Van Allen belts with radiation belts around other planets, scientists can gain insights into the fundamental processes governing planetary magnetospheres.
Conclusion and Broader Implications
The work being conducted by NASA in studying hurricanes, storm clouds, and Earth’s radiation belts highlights the agency’s commitment to advancing our understanding of Earth’s complex climate and space environment. Each of these studies provides valuable data that can inform and improve predictive models, enhance disaster preparedness, and contribute to the safety of human activities in space and on Earth.
Moreover, these studies underscore the importance of continued investment in space-based observation platforms and advanced instrumentation. By leveraging the unique vantage point of space, scientists can observe and analyze phenomena that are otherwise inaccessible or difficult to study from the ground.
As NASA continues to push the boundaries of scientific discovery, the knowledge gained from these efforts will benefit not only the scientific community but also society as a whole. From improving weather forecasts to protecting technological infrastructure, the insights gained from NASA’s research have far-reaching implications that extend beyond the confines of our planet.
For more information on these and other NASA initiatives, you can visit their official website.
For more Information, Refer to this article.