Observations on Mars: New Year and Environmental Changes
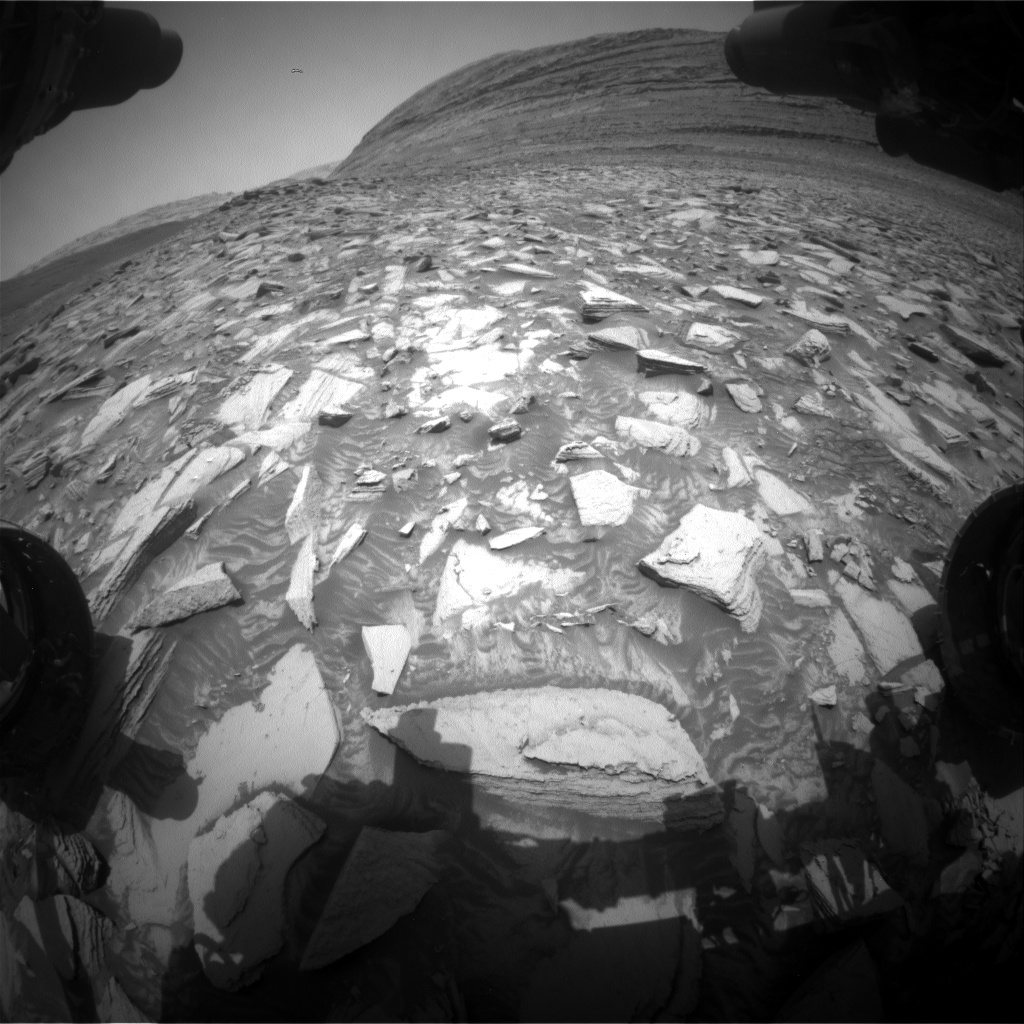
The latest Martian sol, which is equivalent to a day on Mars, kicks off with a fascinating array of environmental science observations. These include images captured by the Navcam, a navigation camera on the Mars rover. The primary focus is on monitoring dust and sand accumulation on the rover’s deck. Additionally, the Navcam is tasked with creating a movie that provides a panoramic view of the northern horizon, aiding in the search for clouds. Recently, cloud sightings have been sparse, but the Martian year is nearing its conclusion, which coincides with the end of the dusty season on Mars.
Understanding the Martian Calendar
The Martian calendar is notably different from Earth’s, with a Martian year lasting 687 Earth days. This extended period is due to Mars taking longer to complete an orbit around the Sun. The current Martian year is about to conclude, and the new year, numbered 38, is set to begin on November 12th. While the cloudy season on Mars won’t reach its peak until February, the phenomenon known as the "noctilucent cloud season" will occur in December and January. Noctilucent clouds are clouds that are illuminated at night, and they have historically provided some stunning images.
Capturing the Martian Skies
In today’s planned activities, the rover will engage in a procedure termed "UltraSPENDI," which stands for "Shunt Prevention ENV Navcam Drop-In." This operation involves capturing 18 movies of clouds and dust devils over a span of three hours. The primary aim of this activity is to prevent the rover’s batteries from staying fully charged for too long. Keeping the batteries at full charge can adversely affect their long-term health, so careful management is necessary.
Why Monitoring Dust and Clouds Matters
Understanding the environment on Mars is crucial for several reasons. Dust and sand can pose challenges for rover operations, including affecting solar panels and moving parts. Monitoring these elements helps scientists make informed decisions about rover maintenance and longevity. Additionally, studying Martian clouds and weather patterns provides insights into the planet’s climate and atmospheric conditions, which are vital for future manned missions.
The Impact of Dust on Mars Rovers
Dust on Mars is more than just an aesthetic concern; it can significantly impact the functionality of equipment. The fine particles can get into joints and moving parts, potentially hindering mechanical operations. Moreover, dust accumulation on solar panels can reduce their efficiency, decreasing the amount of energy available to the rover. By continuously monitoring dust levels, engineers can devise strategies to mitigate these risks.
The Significance of Noctilucent Clouds
Noctilucent clouds on Mars offer a unique opportunity for scientific study. These clouds are typically found at high altitudes and are composed of tiny ice crystals. Observations of these clouds can help researchers understand the dynamics of the Martian atmosphere and the processes that lead to cloud formation. The study of noctilucent clouds might also provide clues about past climatic conditions on Mars and how they compare to Earth’s atmospheric phenomena.
The Role of Navcam in Martian Exploration
The Navcam is an essential tool for the Martian rover, providing both navigational support and scientific data. Its ability to capture high-resolution images and movies allows scientists to observe and analyze the Martian environment in detail. By studying these images, researchers can track changes over time, such as the movement of sand dunes, the development of dust storms, and the appearance and disappearance of clouds.
Preparing for Human Exploration
All these observations and studies are not just for academic interest; they play a crucial role in preparing for future human exploration of Mars. Understanding the planet’s environment, weather patterns, and potential hazards will be vital for ensuring the safety and success of manned missions. The data gathered by current missions lay the groundwork for developing technology and strategies that will enable humans to live and work on Mars.
Reflecting on Past Discoveries
Previous missions have already provided us with a wealth of information about Mars. The rover’s ability to capture and transmit images of noctilucent clouds has been one of the highlights, offering visual evidence of Mars’ dynamic and ever-changing atmosphere. These images not only contribute to our scientific knowledge but also inspire public interest and imagination.
Looking Forward to the New Martian Year
As we approach the end of the current Martian year, there is much anticipation for what the next year will bring in terms of discoveries and advancements. Each year on Mars offers new opportunities to learn and explore, pushing the boundaries of our knowledge about the Red Planet.
The continuous study of Mars, its atmosphere, and its surface conditions is a testament to human curiosity and our quest to understand the universe. As we look to the future, the data collected by rovers and other missions will be invaluable in shaping the direction of space exploration and our understanding of our neighboring planet.
For more detailed information about the current mission and future plans, you can visit the European Space Agency’s official website.
For more Information, Refer to this article.