NASA’s ARCSIX Mission: Unraveling the Mysteries of Arctic Climate Change
In a bid to deepen our understanding of Earth’s rapidly changing climate, NASA has embarked on a new mission that underscores the global significance of the Arctic region. The Arctic Radiation Cloud Aerosol Surface Interaction Experiment (ARCSIX) mission is set to enhance data modeling and offer new insights into the intricate interplay of ice, ocean, and atmospheric conditions in the Arctic. This mission is crucial as the Arctic plays a pivotal role in regulating the Earth’s climate, often likened to the planet’s air conditioner.
The Arctic’s Role in Earth’s Climate System
The Arctic region is integral to Earth’s climate system due to its unique ability to balance the planet’s energy budget. Much of the Sun’s energy, which is absorbed in the tropical regions, is transported to the Arctic by winds and weather systems. Once there, this energy is radiated back into space, effectively cooling the planet. However, the efficiency of this natural air conditioning system is heavily reliant on the presence of sea ice.
Patrick Taylor, a climate scientist at NASA’s Langley Research Center, explains, "More sea ice makes that air conditioning effect more efficient. Less sea ice lessens the Arctic’s cooling effect." Over the past 40 years, the Arctic has experienced significant sea ice loss, resulting in a faster warming rate compared to other parts of the globe. This warming not only affects local weather conditions but also has far-reaching implications, including rising sea levels and increased flooding in distant regions.
The ARCSIX Mission: A Closer Look
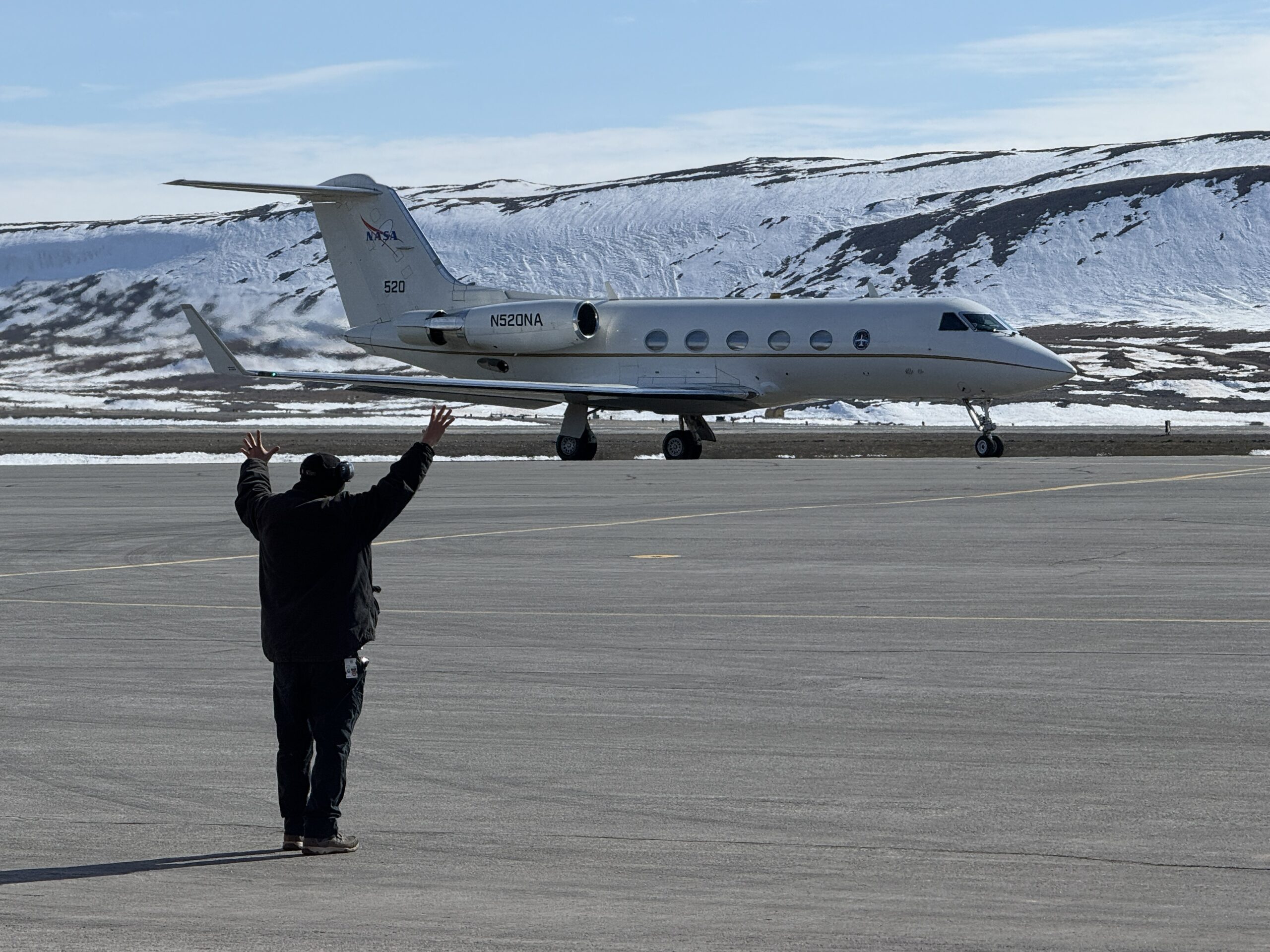
The ARCSIX mission involves flying three aircraft over the Arctic Ocean, north of Greenland. These aircraft are equipped with state-of-the-art instruments designed to gather detailed observations of surface sea ice, clouds, and aerosol particles. These elements are crucial in understanding the Arctic energy budget, which is the balance between incoming solar energy and the energy radiated back into space.
The mission’s first series of flights took place in May and June, coinciding with the onset of seasonal ice melt. The second series of flights began on July 24, during the peak of the summer melt season. This two-phase approach is essential for capturing the dynamic changes in the Arctic environment. Taylor, who is also the deputy science lead for ARCSIX, notes, "The sea ice surface in the spring was very bright white and snow-covered. We saw some breaks in the ice. What we will see in the second campaign is less sea ice and sea ice that is bare, with no snow. It will be covered with all kinds of melt ponds – pooling water on top of the ice – that changes the way the ice interacts with sunlight and potentially changes how the ice interacts with the atmosphere and clouds above."
The Science Behind Sea Ice and Clouds
Sea ice and the snow that blankets it play a critical role in reflecting the Sun’s radiation back into space, thereby cooling the planet. When sea ice diminishes or becomes darker due to melt ponds, more solar energy is absorbed at the surface, potentially altering the local and global climate. Understanding this relationship, particularly the role of clouds in this system, is vital for improving climate predictions.
Linette Boisvert, the cryosphere lead for the mission from NASA’s Space Flight Center, emphasizes the collaborative nature of this mission, "This unique team of pilots, engineers, scientists, and aircraft can only be done by leveraging expertise from multiple NASA centers and our partners. We gathered great data of the snow and ice pre-melt and at the onset of melt. I can’t wait to see the changes at the height of melt as we measure the same areas covered with melt ponds."
Unexpected Discoveries and Ongoing Research
The ARCSIX mission has already yielded intriguing findings. In collaboration with the University of Colorado Boulder, the research team discovered what Taylor refers to as a “sea ice sandwich” – a younger layer of sea ice trapped between two older layers. Additionally, the team observed more drizzle within the clouds than anticipated. These unexpected findings warrant further investigation as the data is fully processed.
Another surprising observation came from a volcano eruption in Iceland. Taylor explains, "A volcano erupted in Iceland, and we believe the volcanic aerosol plume was indicated by our models four days later. Common scientific knowledge tells us volcanic particles, like ash and sulfate, would have already been removed from the atmosphere. More work needs to be done, but our initial results suggest these particles might live in the atmosphere much longer than previously thought."
Previous research has shown that aerosol particles in clouds can influence sea ice melt. Data from the ARCSIX spring flights revealed multiple layers of aerosol particles in the Arctic atmosphere, including wildfire smoke, pollution, and dust transported from Asia and North America. These particles can have varying effects on cloud formation and behavior, which in turn affects the melting of sea ice.
Future Implications and Predictive Models
The data collected during the ARCSIX mission is expected to significantly enhance our understanding of Arctic climate dynamics. Taylor is optimistic about the mission’s contributions, stating, "We got everything we hoped for and more in the first campaign. The data from this summer will help us better understand how clouds and sea ice behave. We’ll be able to use these results to improve predictive models. In the coming years, scientists will be able to better predict how to mitigate and adapt to the rapid changes in climate we’re seeing in the Arctic."
Improved predictive models will be invaluable for policymakers and communities worldwide as they prepare for and respond to the impacts of climate change. The ARCSIX mission exemplifies the importance of continued scientific research and international collaboration in addressing one of the most pressing challenges of our time.
Additional Resources
For those interested in learning more about the ARCSIX mission and its findings, NASA provides a wealth of information on their dedicated pages:
- ESPO.NASA.gov
- AIR.LARC.NASA.gov
- NASA.gov/Earth
By exploring these resources, readers can gain a deeper appreciation of the groundbreaking work being done to understand and address the complexities of Arctic climate change.
In conclusion, the ARCSIX mission stands as a testament to the critical role of scientific inquiry in unraveling the mysteries of our planet’s climate system. As the Arctic continues to warm at an unprecedented rate, missions like ARCSIX are essential for developing the knowledge and tools needed to navigate our rapidly changing world.
For more Information, Refer to this article.