NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley is celebrating its 85th anniversary, marking nearly a century of groundbreaking contributions to science, engineering, research, and innovation. This year, the center has been involved in numerous projects and achievements that align with its longstanding tradition of advancing space exploration and technology. Let’s delve into some of the highlights from 2024, showcasing Ames’ diverse and impactful work.
### Unveiling the Mysteries of the Artemis I Heat Shield
One of the significant challenges faced by NASA involved understanding the unexpected char loss on the Artemis I Orion spacecraft’s heat shield. Researchers at Ames played a crucial role in this investigation. Utilizing the Avcoat material response data from Artemis I, the team recreated the entry trajectory environment within NASA Ames’ arc jet facilities. This effort was pivotal in identifying the root cause of the heat shield’s performance issues, showcasing Ames’ expertise in simulating real-world conditions and solving complex aerospace problems.
### Advancements in Spacecraft Swarming Technologies
The Starling spacecraft swarm has successfully achieved its primary mission objectives after ten months in orbit. This accomplishment highlights the potential of swarm configurations in low Earth orbit, which include autonomous decision-making and efficient information distribution. Such advancements are critical for future space missions, where multiple spacecraft can work together to achieve complex tasks, enhancing our capabilities in space exploration.
### Pioneering Nutrient Production for Long-Duration Space Missions
NASA’s BioNutrients project is entering its fifth year, focusing on the ability of microorganisms to produce essential nutrients on-demand for astronauts during long-duration space missions. This research is vital for the health of astronauts in space and has reached a significant milestone. Researchers have successfully processed production packs on Earth and aboard the International Space Station simultaneously, demonstrating the feasibility of producing nutrients after extended periods in space. This breakthrough offers confidence in supporting future crewed missions, such as those to Mars.
### Enhanced Data Visualization with Upgraded Hyperwall
Ames has upgraded its hyperwall, a massive 300-square-foot wall of LCD screens that displays high-resolution visualizations of large datasets produced by NASA supercomputers. This advanced visualization tool allows researchers to better comprehend complex data and advance NASA’s various missions. The hyperwall exemplifies how high-end computing technology can facilitate understanding and drive innovation in scientific research.
### Artificial Intelligence Initiatives
Ames is at the forefront of NASA’s artificial intelligence (AI) efforts, contributing to research, development, and agency-wide collaboration. This year, NASA appointed David Salvagnini as its first chief artificial intelligence officer and hosted its inaugural agency-wide town hall on AI. These initiatives focus on safely developing AI technologies to advance NASA’s missions, demonstrating the agency’s commitment to integrating AI into its operations.
### Solar Sailing: A New Era of Space Propulsion
The Advanced Composite Solar Sail System, launched from Māhia, New Zealand, represents a new frontier in propulsion technology. The small satellite, using lightweight composite booms to support a reflective polymer sail, harnesses sunlight pressure to propel itself. This innovative approach to space travel promises a more sustainable and efficient means of exploration, potentially transforming how future missions are conducted.
### Innovations in Earth and Ocean Research
Ames researchers have been deeply involved in studying Earth’s oceans and waterways, contributing to projects like NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission and engaging students in Puerto Rico with oceanography and coral reef preservation. Collaborations with partners have enhanced ecosystem management, combining satellite measurements with animal tracking data. Additionally, in partnership with the U.S. Geological Survey, specialized instruments are being tested to monitor river flow changes, highlighting Ames’ commitment to understanding and preserving our planet’s natural resources.
### Unraveling the Mysteries of Mars’ Moons
Through supercomputer simulations, Ames researchers have proposed a new theory about the formation of Mars’ moons, suggesting that the process began with the destruction of an asteroid. Furthermore, using the James Webb Space Telescope, Ames scientists have identified the smallest asteroids in the main asteroid belt, contributing to our understanding of the solar system’s formation and evolution.
### Thermal Protection Innovations
A heat shield material developed at Ames, known as C-PICA (Conformal Phenolic Impregnated Carbon Ablator), played a crucial role in the safe return of a spacecraft from Varda Space Industries. This marked the first time a NASA-manufactured thermal protection material returned from space, demonstrating Ames’ leadership in developing materials that enhance spacecraft safety and performance.
### HelioSwarm and CAPSTONE Missions
The HelioSwarm mission, comprising nine spacecraft, aims to provide deeper insights into our universe and protect astronauts, satellites, and communication signals. Meanwhile, the CAPSTONE CubeSat continues to orbit the Moon in a unique path, supporting future lunar missions and the Gateway project, which is part of NASA’s Artemis campaign.
### Advancements in Air Traffic Management and Drone Technology
NASA’s efforts in air traffic management have paved the way for approved package delivery drone flights in Dallas, showcasing the potential for integrating drones into our airspace. Additionally, partnerships with AeroVironment and Aerostar have led to demonstrations of new air traffic management concepts, ensuring the safe operation of aircraft at higher altitudes and contributing to fuel savings and reduced flight delays at major airports.
### BioSentinel: A Frontier in Solar Radiation Research
The BioSentinel satellite, launched aboard NASA’s Artemis I, is over 30 million miles from Earth, studying solar radiation storms in space. This research is crucial for understanding the effects of solar storms and their impact on life beyond Earth, providing valuable data for future deep space missions.
### Firefighting Innovations with Drones and Balloons
NASA is developing technologies to enable drones to monitor and combat wildland fires around the clock. The ACERO project aims to enhance fire coordination and operations using advanced aviation technologies. Additionally, the STRATO project utilizes high-altitude balloons to improve communication among firefighters, increasing safety and efficiency in fire management.
### A New Visitor Experience at Ames
The NASA Ames Visitor Center at the Chabot Space & Science Center offers a reimagined, immersive experience with new exhibits and interactive displays. Visitors can engage with simulations that allow them to design and test rovers, planes, and robots for space exploration, fostering interest in STEM fields and offering a glimpse into the work of NASA scientists.
### Collaborative Efforts in Cancer Research and Supercomputing
NASA Ames continues to collaborate with academic institutions like the University of California, San Francisco, and Berkeley. These partnerships explore research opportunities in cancer treatment and provide supercomputing resources to support scientific advancements. Such collaborations exemplify NASA’s commitment to using its resources and expertise for the greater good.
### The Legacy and Future of Ames Research Center
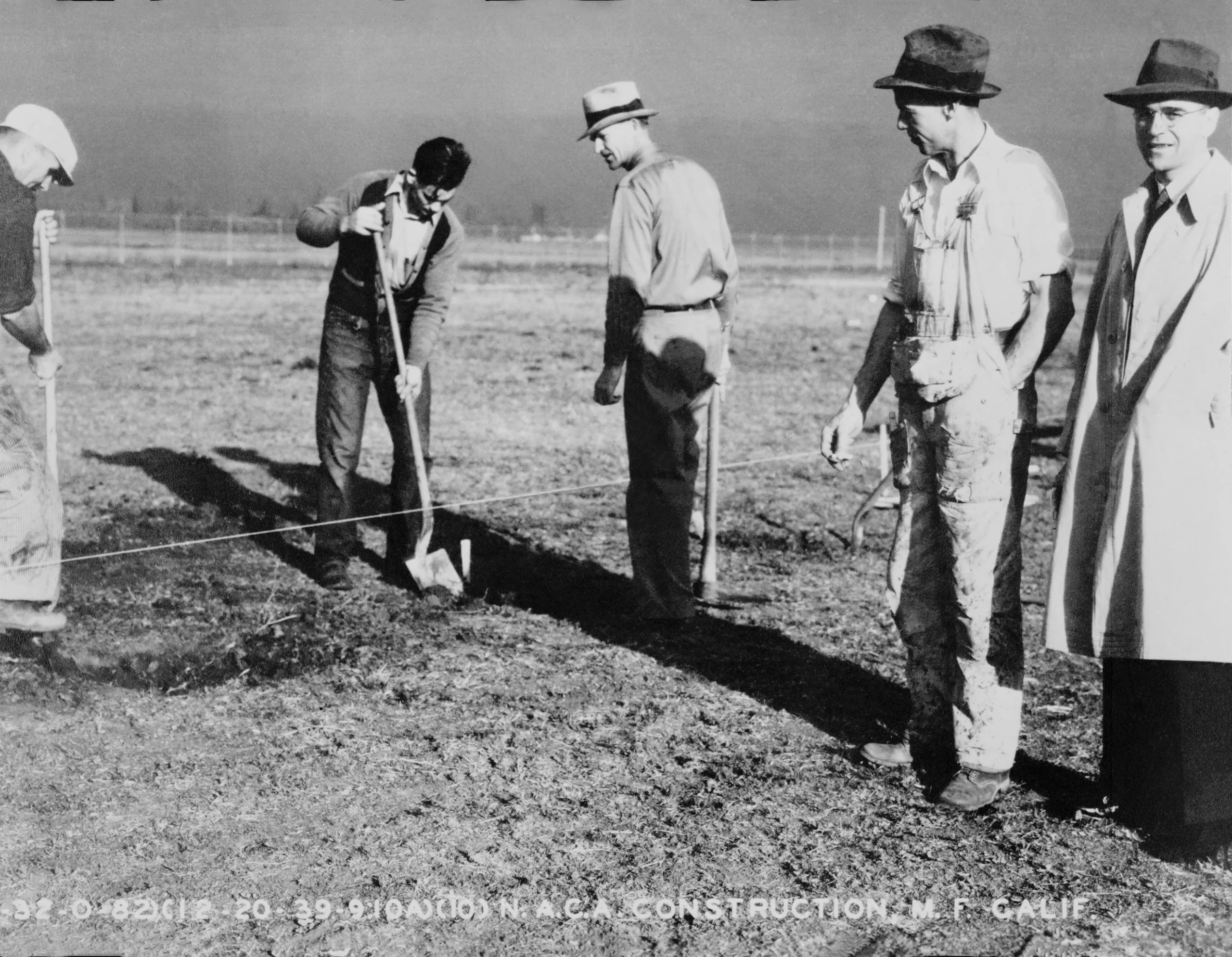
Founded as the Ames Aeronautical Laboratory in 1939, the center has a rich history of innovation and scientific discovery. Over the years, Ames has maintained a commitment to fostering an environment of intellectual freedom and collaboration, attracting some of the brightest minds in science and engineering. Researchers at Ames are encouraged to pursue high-risk, high-reward ideas, contributing to technological breakthroughs that have enabled humanity’s exploration of space and improved life on Earth.
Looking forward, the potential for advancements in technology and research at Ames is as vast as space itself. The center remains dedicated to its mission of pushing the boundaries of science and technology, ensuring that future generations benefit from its ongoing contributions to space exploration and innovation.
For more detailed insights into the exciting work at Ames, visit NASA’s official website.
For more Information, Refer to this article.