Understanding Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
The global energy landscape is evolving rapidly, and with it, the technologies that drive energy generation are also advancing. Among these innovations, Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) have emerged as a significant development in nuclear power technology. SMRs are essentially a type of nuclear reactor that is smaller in size compared to traditional nuclear reactors. They offer several advantages, including enhanced safety features, scalability, and flexibility in deployment. This article seeks to explore what SMRs are, their potential impact on the energy sector, and recent developments that highlight their growing prominence.
What are Small Modular Reactors?
Small Modular Reactors are a new class of nuclear reactors that are designed to be compact and scalable. Unlike traditional nuclear reactors, which can be massive and require significant infrastructure, SMRs are smaller and can be manufactured in a factory setting, which allows for easier transport and installation. This modular approach not only reduces construction times but also lowers the initial capital investment required, making nuclear power more accessible.
The design of SMRs incorporates advanced safety features. For instance, many SMR designs use passive safety systems that do not require active controls or human intervention to shut down safely in the event of an emergency. This intrinsic safety is a key selling point, as it addresses some of the public concerns associated with nuclear energy.
The Growing Interest in SMRs
Recently, there has been a notable surge in interest in SMRs from countries around the world. This interest stems from the need to find sustainable and low-carbon energy solutions to meet growing electricity demands while also reducing greenhouse gas emissions. SMRs are seen as a viable option for achieving these goals because they can be deployed in a variety of settings, including off-grid locations and developing regions with limited infrastructure.
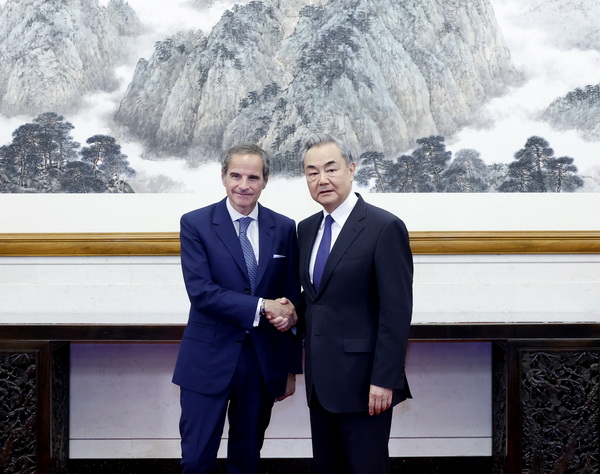
During a recent event, Mr. Rafael Mariano Grossi, Director General of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), highlighted the progress being made in the deployment of SMRs. He presented a user requirements document that outlines the key needs and expectations for SMRs, covering aspects such as design, safety, and regulatory compliance. This document serves as a guideline for countries and companies looking to invest in SMR technology, ensuring that the reactors meet the highest standards of safety and efficiency.
China’s Role in SMR Development
China has emerged as a leader in the development and deployment of SMRs. According to Mr. Grossi, China is making considerable strides in this area, marking an important step toward the safe and effective implementation of SMR technology. The country has been investing heavily in nuclear power as part of its broader strategy to diversify its energy sources and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
During a meeting with Shan Zhongde, the new Chairman of the China Atomic Energy Authority (CAEA), Mr. Grossi acknowledged China’s pivotal role in the peaceful use of nuclear science and technology. China’s advancements in nuclear energy extend beyond power generation to include medical applications, agricultural improvements, and other areas that benefit from nuclear technology.
Benefits and Challenges of SMRs
The deployment of SMRs offers numerous benefits. They provide a reliable source of low-carbon energy that can complement renewable energy sources like wind and solar. This is particularly important for regions where renewable energy alone cannot meet the entirety of energy demand. Additionally, the modular nature of SMRs allows for flexible scaling, meaning that additional modules can be added as demand grows.
However, there are challenges to consider. The regulatory landscape for SMRs is still evolving, and international cooperation is required to ensure these reactors meet stringent safety standards. Furthermore, public perception of nuclear energy remains a hurdle, with concerns over safety and waste management needing to be addressed transparently.
The Future of SMRs
As the world continues to grapple with the dual challenges of energy security and climate change, SMRs represent a promising solution. Their ability to provide stable, low-emission power makes them an attractive option for countries looking to transition away from fossil fuels. The IAEA’s efforts in providing guidance and support for SMR development are crucial in facilitating this transition.
With ongoing research and development, the technology underpinning SMRs is expected to evolve further, enhancing their efficiency and reducing costs. As more countries express interest in SMRs, international collaboration will be key to overcoming technical and regulatory hurdles. The future of SMRs holds great potential, and continued advancements in this field could play a significant role in shaping the global energy landscape.
For more detailed information, you may refer to the original article on the IAEA website.
For more Information, Refer to this article.