You can use safe mode to help you resolve issues that might keep your Mac from completely starting up. Safe mode is a cure to hundreds of problems in Mac. Also, the safe mode in Mac is different from Safe mode in Windows as it also tries to resolve lots of problem tat it finds. Let’s discuss in detail – What is safe mode and how to start your Mac in safe mode?
What is safe mode?
Safe mode (sometimes called safe boot) is a way to start up your Mac so that it performs certain checks, and prevents some software from automatically loading or opening. Starting your Mac in safe mode does the following:
- Verifies your startup disk, and attempts to repair directory issues if needed
- Only essential kernel extensions are loaded- (a.k.a. ketxs, or hardware and software drivers), No third party items
- Prevents Startup Items and Login Items from opening automatically
- Disables user-installed fonts
- Deletes font caches, Kernel cache and other system cache files
- Together, these changes can help resolve or isolate issues related to your startup disk.
And it’s very simple to start your Mac in Safe Mode, either using your keyboard or by entering a command in Terminal.We will learn different way of starting your Mac in Safe Mode later in this post.
When and why should we start Mac in Safe Mode?
When you have some problem with your mac the first troubleshooting you do is restart the Mac.
Most of the time, your Mac just works after restarting.
But there will be times when a rogue app, a misbehaving service, outdated caches and other issue will cause your Mac to slow, stop starting up or exhibit other unwanted symptoms. Thankfully, Apple has provided a way to boot OS X in Safe Mode.
Although booting in Safe Mode on a daily basis—or whenever an insignificant problem arises— isn’t recommended, there are definitely instances when starting up in Safe Mode could be your last resort.
Here are some of the typical scenarios:
If your Mac doesn’t finish starting up—Certain issues might keep your Mac from completely starting up and using Safe Mode can help you resolve them.
If an app is causing issues— An app you recently installed might be the culprit, especially if it came outside the Mac App Store. Starting up in Safe Mode might help isolate the misbehaving app as it prevents certain software from automatically loading or opening.
If your Mac is running slow— Just like Windows, your Mac also creates temporary files and various caches over time which might slow down the overall performance of the operating system and apps. These unnecessary files are safely cleaned from Mac when started in safe Mode.
If your Mac has directory issues—Many, but not all issues with your Mac’s startup disk can be resolved using the built-in Disk Utility application. If you’re plagued with an issue that cannot be reproduced in Safe Mode but appears to be resolved when you start up normally, chances are it was caused by a cache or a directory issue with your startup disk that Safe Mode fixed.
How to Start your Mac in Safe Mode?
Starting up in safe mode
- Follow these steps to start up into safe mode.
- Start or restart your Mac.
- Immediately after you hear the startup sound, press and hold the Shift key.( Note:- If you are using a Wireless Keyboard,Make sure you press the Shift Key immediately after you hear the start up chimes sound.Bluetooth controllers will only activate after the startup chimes sound, so if the key is held before this, the key press will not be recognized. ).
- Release the Shift key when you see the Apple logo appear on the screen.
 |
| Start your Mac in Safe Mode |
- After the Apple logo appears, it might take longer than usual to reach the login screen or your desktop. This is because your Mac performs a directory check of your startup disk as part of safe mode.

Start your Mac in Safe Mode - To leave safe mode, restart your computer without pressing any keys during startup.
If you’re using FileVault
If your startup disk is encrypted with FileVault, you can still hold down the Shift key immediately after powering on your Mac to start up in safe mode. You might be prompted to log in twice as part of this process – first to unlock the startup disk, and a second time to log into the Finder. You can let go of the Shift key after you see the first login screen.
If an issue doesn’t happen in safe mode
If an issue doesn’t happen when your Mac is started in safe mode, try restarting again without pressing any keys at startup. If the issue appears to be resolved when you start up normally, it was possibly caused by a cache or a directory issue with your startup disk that safe mode fixed.
If you restart your Mac normally and an issue comes back when you reach your desktop, try disabling any login items that automatically open when you log in.
If your Mac restarts or shuts down in safe mode
If your Mac automatically restarts in safe mode, OS X might have found an issue that it’s trying to fix.
Safe mode performs a directory check of your startup disk, similar to what happens when you choose to verify or repair a disk using Disk Utility. If OS X finds an issue, the directory on your startup disk is repaired and your Mac restarts.
If your Mac turns itself off when you start up in safe mode, check the power connection on your Mac to make sure it’s plugged in securely at both your Mac and the power outlet. If you’re using a MagSafe power adapter, make sure the LED on your power adapter is yellow or green. Then, try starting up in safe mode again.
If your Mac repeatedly restarts or shuts down during safe mode, contact Apple Support, or consult with an Apple Authorized Service Provider or Apple Genius for more help.
Is your Mac taking longer than usual to boot in Safe Mode?
This is normal.Your Mac performs a directory check of your startup disk as part of Safe Mode so it will take a significantly longer time than usual to reach the login screen or the desktop
3 ways of identifying if you’re started in Safe Mode
If you’re unsure as to whether or not you’re in Safe Mode, take note of the following signs that give it away.
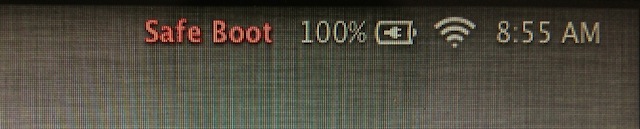
1. Menu bar reads “Safe Boot”
 |
| Start your Mac in Safe Mode |
The first indication that you’re starting up in Safe Mode appears when you land on the login screen. If you’re in Safe Mode, the words “Safe Boot” in red letters will appear in the menu bar in the upper right corner of the screen.
2. Slower overall performance
Past the login screen, you’ll notice slower overall performance. Graphics will no longer be accelerated as default drivers are loaded. The OS X menus, windows and the Dock appear solid even if Translucent Menu Bar is selected in System Preferences.
Your screen might blink or tear during the login process. OS X menus, the Dock, your desktop and other aspects of the user interface won’t have as many visual effects and translucency will be disabled.
And as mentioned further below, several OS X features might be unavailable to you in Safe Mode, like watching movies in the DVD Player app, capturing video, connecting to Wi-Fi networks and more.
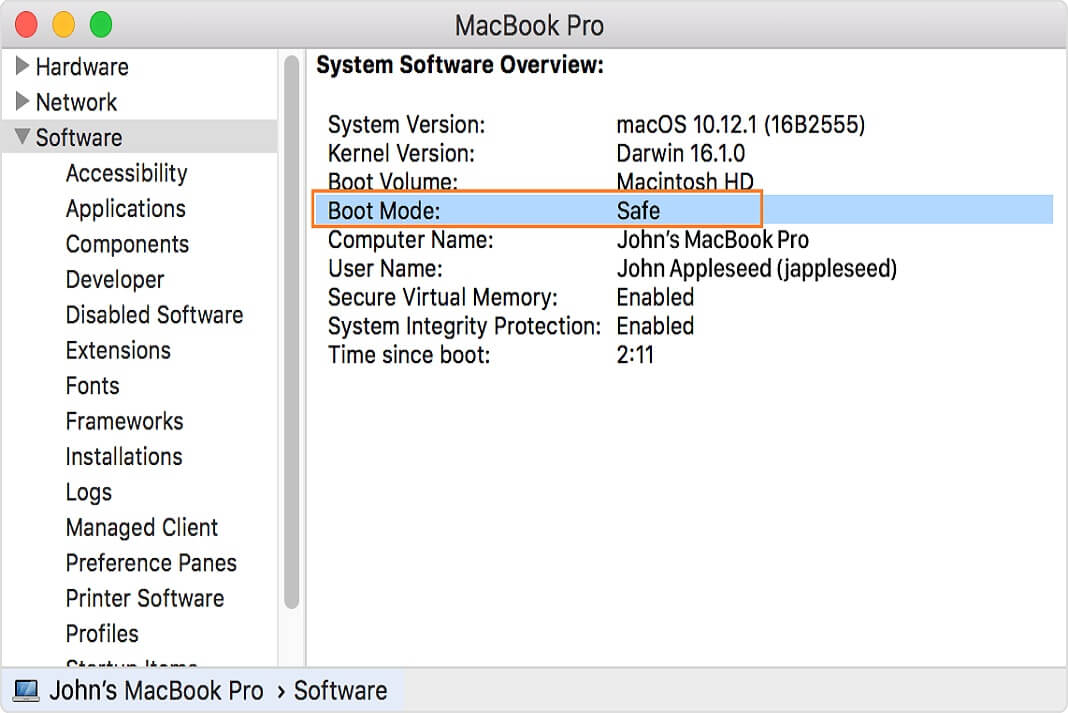
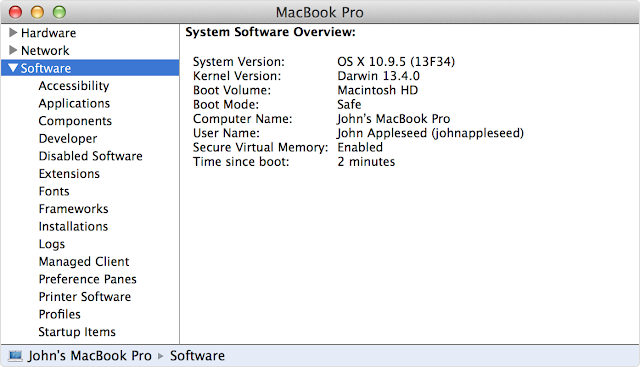
3. Boot Mode in System Information reads “Safe”
 |
| Start your Mac in Safe Mode |
Another method of determining the status of your boot mode involves using the System Information application.
Step 1: Open System Information from Applications > Utilities. You can also choose About This Mac from the Apple menu and then click the System Report button in the Overview section.
Step 2: In the lefthand column, locate and click the Software section. You should see a couple related items listed on the right side of the System Information window.
If the Boot Mode is listed as “Safe” you’re started in Safe Mode. If it reads “Normal,” you’re in OS X’s normal-boot mode.
Some features aren’t available in safe mode
Some features of your Mac aren’t available when it’s started in safe mode, so after you’re done using safe mode you should restart your computer normally.
For example, these features don’t work in safe mode:
- You can’t play movies in DVD Player.
- You can’t capture video in iMovie and some other video apps.
- Some audio input or output devices might not work.
- Some USB, FireWire and Thunderbolt devices might not be available.
- Wi-Fi networking might be limited or unavailable depending on the Mac and OS X version you’re using.
Safe mode in OS X v10.5 or later also disables accelerated graphics. This makes the OS X menu bar appear solid even if “Translucent Menu Bar” is selected in System Preferences. Your screen might also “blink” or “tear” during login when your Mac is started in safe mode.
Safe mode in OS X v10.6 or later also disables File Sharing.
Starting in safe mode without a keyboard
If your Mac doesn’t have a keyboard available to start in safe mode but you have remote access to it, you can configure the Mac to startup in safe mode using the command line.
Access the command line by either opening Terminal remotely, or by logging into the computer using SSH.
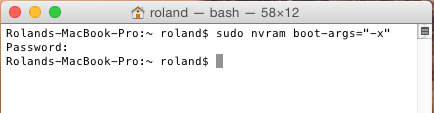
Use the following Terminal command and restart your Mac:
sudo nvram boot-args=”-x”
 |
| Start your Mac in Safe Mode |
Unfortunately it is a bit difficult to see if this is the case when the system is only displaying a gray progress bar; however, you can force the system to show you what is going on by having it boot to both Safe and Verbose modes at the same time.If you want to start in verbose mode as well, use this instead:
sudo nvram boot-args=”-x -v”
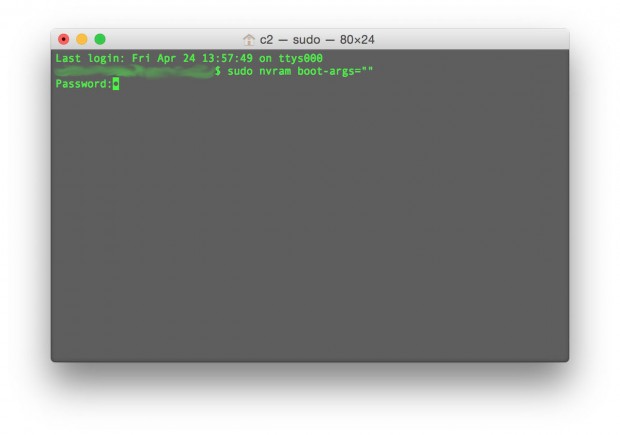
To restart your Mac normally from Safe Mode.After using safe mode, use this Terminal command to return to a normal startup:
sudo nvram boot-args=””
 |
| Start your Mac in Safe Mode |
Note :- You can replace the “v” with an “s” to tell it to use “Single User” mode instead (they should be equivalent for this purpose):
sudo nvram boot-args=”-x -s”
Incoming Search Terms
Mac in Safe Mode
Safe mode command for Mac
how to start mac in safe mode
mac verbose safe mode
single user mode
repair mac in safe mode
Safe Mode fix many issue in Mac