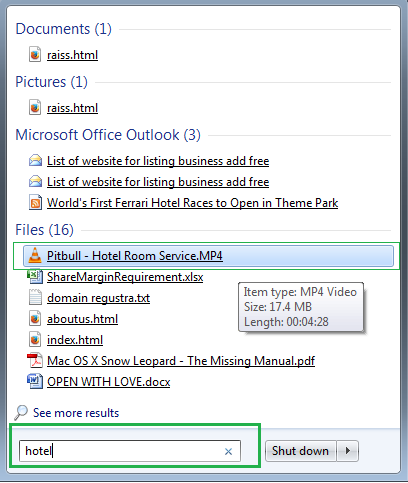
Searching feature in windows is one of the greatest advantage. It lets you access your files quickly and easily without you peeping into different folders one by one.It very useful when you have forgot the place of the file or the exact name of the file.Have you ever wondered how this search option is powered or built.It is actually built or powered by Indexing in Windows just like an index of a book.But here in windows you can choose the location to include or exclude in indexing.Or you can delete or add entry or remove old unavailable entry or rebuild the whole index to optimize the search feature for enabling the fast searching.
What is Index?
A collection of detailed information about the files on your computer. Windows uses the index to perform very fast searches on your computer. Here are some advanced indexing settings you can change.
What files are indexed?
By default, all of the most common files on your computer are indexed. Indexed locations include all folders included in libraries (anything you see in the Documents library, for example), e‑mail, and offline files. Files that aren’t indexed include program files and system files—files that most people rarely need to search.
Can I index my entire computer so all searches are fast?
You shouldn’t do this. If you make the index too large, or if you include system file locations (such as the Program Files folder), your routine searches will slow down. For best search results, we recommend that you only add folders that you search frequently to enable fast searching.
What if I’m using Windows Server 2008 R2?
How to fix Searching and Indexing issue
1. To add a file type to the index
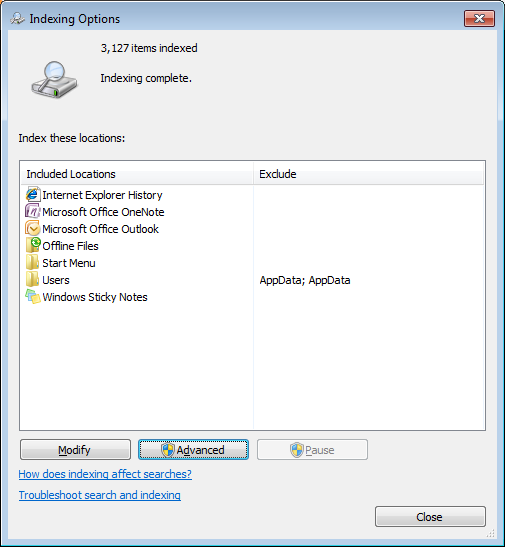
- Open Indexing Options from control panel.
- Click Advanced.
- In the Advanced Options dialog box, click the File Types tab.
- In the Add new extension to list box, type the file name extension (for example, “txt”), and then click Add to enable searching the file type.
Fix Searching and Indexing issue and Rebuild the Index
- Click Index Properties Only or Index Properties and File Contents, and then click OK.After this method you should be able to search the added file type.
2. To rebuild the index
- Go to Control panel and then open Indexing Options.
- Click Advanced.
Rebuilding the Index on Windows PCs - In the Advanced Options dialog box, click the Index Settings tab, and then click Rebuild. If you are prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
3. To index encrypted files for searching encrypted files too
Before you add encrypted files to the index, we recommend that you have Windows BitLocker (or a non-Microsoft encryption program) enabled on your system drive (the drive that Windows is installed on).
Note:Windows BitLocker is only included in Windows 7 Enterprise and Windows 7 Ultimate.
Note that the index will automatically rebuild each time this setting is changed. This can take a long time, and might cause searches to be incomplete until the process is complete.
- Go to Control panel and then open Indexing Options.
- Click Advanced. If you are prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
- In the Advanced Options dialog box, click the Index Settings tab, select the Index encrypted files check box, and then click OK. If you are prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
Notes
Although you can use a non-Microsoft program to encrypt your system drive, non-Microsoft file encryption programs are not supported. Windows only supports files encrypted using Encrypting File System (EFS).
EFS is only included in Windows 7 Enterprise, Windows 7 Professional, and Windows 7 Ultimate.
If you add encrypted files to the index and you’re not using full-volume encryption for the location of the index, encrypted data from your files for example, text from an encrypted Microsoft Word document will be added to the index and will be available for searching. The index is obscured so that it’s not easily readable if someone tries to open the index files, but it doesn’t have strong data encryption. If someone were to gain access to your computer, they could extract your data from the index. Therefore, the location of the index should also be encrypted to help protect your indexed data.
4. To index words with and without diacritics as different words
If you commonly use diacritics (small signs added to letters to change the pronunciation of words) in your file and folder names, you can configure the index to recognize words with diacritics differently. By default, Windows recognizes diacritics according to the language version you are using. If you change this setting, all diacritics will be recognized.
The index will automatically be rebuilt each time this setting is changed. This can take a long time and might cause searches to be incomplete until the process is complete.
- Click to open Indexing Options.
- Click Advanced. If you are prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
- In the Advanced Options dialog box, click the Index Settings tab.
- Under File Settings, select the Treat similar words with diacritics as different words check box, click OK, and then click OK again.
5. To change the location where the index is stored
If you need to free up space on a hard disk, you can change the location of the index. If you change this location, the Windows Search service will automatically be restarted, and the change will not go into effect until the restart is complete.
- Click to open Indexing Options.
- Click Advanced. If you are prompted for an administrator password or confirmation, type the password or provide confirmation.
- In the Advanced Options dialog box, click the Index Settings tab.
Location of Index File
- Under Index location, click Select new, click a new location, click OK, and then click OK again.
Note: When you change the index location, you should choose a location on a non-removable hard disk that is formatted using the NTFS file system.
What does it mean when I see a message that search results might be incomplete?
It means that the files are still being indexed. To perform fast and accurate searches, Windows collects information about files on your computer. This information is stored in the index. Periodically, Windows needs to update the index. If you perform a search while the index is being updated, the results might be out of date.
What does it mean when I see a message that a location can’t be searched or there’s no media present in the search location?
There’s a problem searching one or more of your selected locations. Usually that’s because you’ve selected a network location or a device that’s not currently connected to your computer. It’s also possible that you’ve selected a removable media device with no media (such as a memory card or a CD) in the device. Check your locations, and then try the search again.
How do I troubleshoot problems with searching and indexing?
If you are experiencing problems with searching, such as unusually slow searches or incomplete search results,or no search results at all run the Search and Indexing troubleshooter to see if it can diagnose the problem.
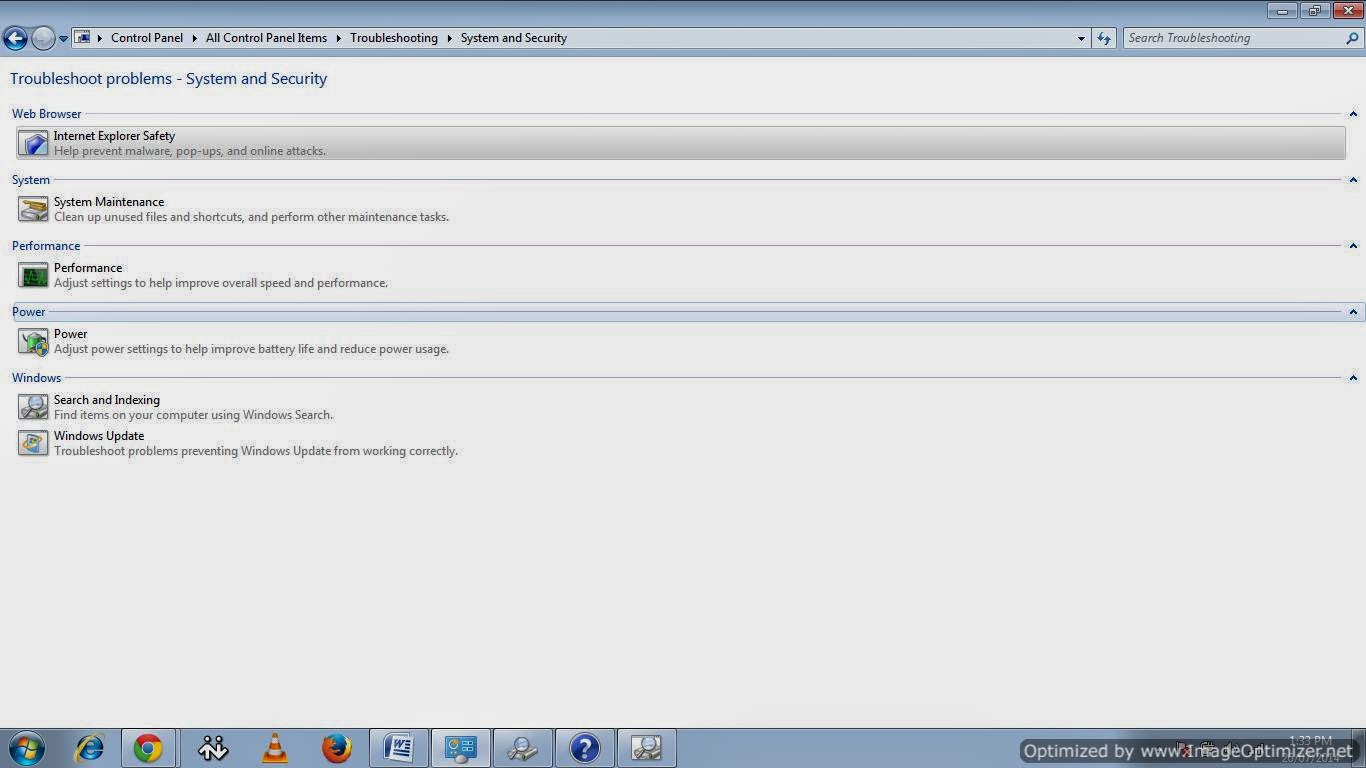
- Go to control panel and open Troubleshooting.
- Click on System and Security.

Fix Searching and Indexing issue and Rebuild the Index
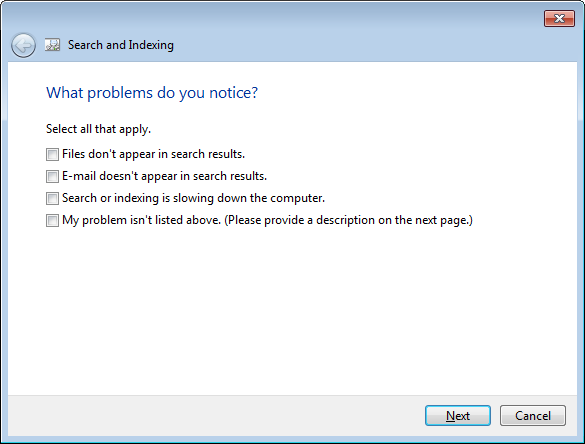
- Now Click on Search and Indexing.
- It’s gonna ask the problem you are facing so select the problems and click next to troubleshoot and fix.

Fixing Searching and Indexing Issue by Troubleshooter
Depending on the severity of the problem, the Search and Indexing troubleshooter might need to restart the Windows Search service. After the Windows search service it restarted it might take few minutes to enable searching feature.
Here is a list that troubleshooter checks and fix
| ||||
When permissions on the Windows Search data directories are set incorrectly, the search service might not be able to access or update the computer’s search index. This can result in slow searches or incomplete search results. | ||||
| ||||
Problems with the Search Filter Host might indicate errors in the Windows Search service, which can cause searches to fail or return incomplete search results. | ||||
| ||||
When the Windows Search service is forcibly shut down while performing maintenance, searches might fail or return incomplete search results. | ||||
| ||||
When the Windows Search service is forcibly shut down, searches might fail or return incomplete search results. | ||||
| ||||
When the Windows Search service is not running, searches might be slower, and you might not be able to find all items. | ||||
| ||||
Problems with the Windows Search service can cause searches to fail or return incomplete search results. | ||||
| ||||
Problems with the Search Protocol Host might indicate errors in the Windows Search service, which can cause searches to fail or return incomplete search results. |




































Nicely written…I never knew this