Since 1970, the global wildlife population has experienced an alarming decline, with an average decrease of 73% in populations of mammals, birds, fish, reptiles, and amphibians. This significant reduction is symptomatic of worsening environmental conditions exacerbated by climate change, water scarcity, and the relentless depletion of natural resources. The stakes are high; approximately 55% of the world’s GDP, which is about $58 trillion, is at risk due to this ongoing environmental degradation. Immediate action is imperative to curb this decline and safeguard the planet’s ecological and economic future.
Over the past two decades, substantial efforts have been made to develop tools and technologies that assist governments, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), and academic institutions worldwide in addressing the pressing issues of nature and biodiversity loss. Today, we are excited to share three new initiatives aimed at accelerating the protection and restoration of nature, particularly in regions that are home to some of the most vital habitats, ecosystems, and communities.
Google for Startups Accelerator: AI for Nature and Climate
One of the significant developments in the fight against environmental degradation is the launch of the Google for Startups Accelerator focused on AI for Nature and Climate. This initiative is designed to empower startups that are using artificial intelligence (AI) to address environmental challenges. It provides these startups with the necessary resources, mentorship, and technology to enhance their solutions, thus fostering innovation in the field of environmental conservation.
AI for Nature and Climate: A New Grant Fund for Nonprofits
In a move to bolster AI-driven conservation efforts, Google.org has committed $3 million to the Instituto Clima e Sociedade (iCS) to initiate an open call for grant submissions. This funding is specifically targeted at Brazilian nonprofit organizations and research centers that are developing AI-enabled solutions. The grant aims to support projects in three primary areas:
- Reversing Biodiversity Loss: This includes initiatives that align with the "30×30" global effort, which aims to protect 30% of Earth’s land and oceans by 2030. Such projects focus on biodiversity protection and the establishment of protected areas and Indigenous territories, adhering to the Global Biodiversity Framework.
- Bioeconomy: This area covers technologies that enhance the value chains of timber and non-timber forest products, as well as services linked to Brazil’s socio-biodiversity. The objective is to support sustainable economic activities that contribute to environmental conservation.
- Regenerative Agriculture: Emphasis is placed on supporting regenerative and resilient agricultural practices, particularly for small-scale farmers. These practices are crucial for maintaining healthy ecosystems and ensuring food security in the face of climate change.
For those interested in learning more about this funding opportunity and its areas of focus, additional information is available on the dedicated website.
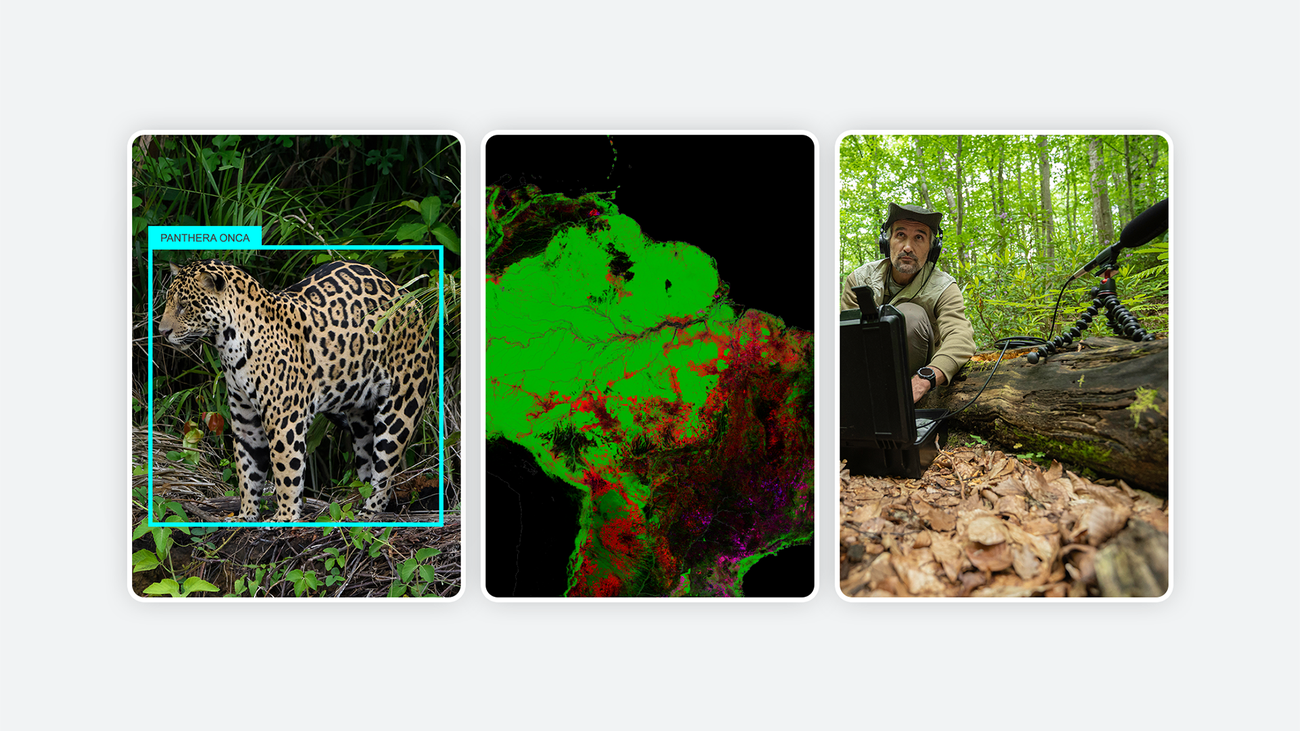
SpeciesNet: A New Open Source AI Model for Wildlife Conservation
Another groundbreaking announcement is the release of SpeciesNet, an open-source AI model designed to enhance wildlife conservation efforts. SpeciesNet is capable of identifying animal species by analyzing photographs taken by camera traps. Since its inception in 2019, this AI model has been utilized by thousands of wildlife biologists via a Google Cloud-based tool known as Wildlife Insights. This tool has significantly streamlined biodiversity monitoring and informed conservation decision-making processes.
The open-source release of SpeciesNet is expected to have a profound impact, enabling tool developers, academics, and biodiversity-focused startups to expand biodiversity monitoring capabilities in natural habitats. By making this advanced technology widely accessible, it is hoped that more comprehensive data can be gathered, leading to better-informed conservation strategies.
The Importance of Protecting Nature and Biodiversity
Protecting nature and preserving biodiversity are critical components of the broader strategy to combat climate change. The degradation of natural ecosystems not only threatens the survival of countless species but also undermines the ecological services these systems provide, such as carbon sequestration, water purification, and soil fertility. These services are essential for maintaining the balance of our planet’s climate and ensuring the well-being of human societies.
The initiatives announced today represent a significant step forward in the global effort to address these challenges. By leveraging cutting-edge technology and fostering collaboration among diverse stakeholders, there is hope for a more sustainable future where both nature and humanity can thrive.
Reactions and Reflections
The announcement of these initiatives has been met with positive reactions from environmentalists and conservationists around the world. Many see this as a crucial step towards integrating technology and environmental science to create innovative solutions for pressing ecological issues. The use of AI in this context is particularly promising, as it offers the potential to process and analyze large datasets efficiently, thereby enhancing our understanding of complex ecological systems.
Moreover, the focus on supporting startups and nonprofit organizations underscores the importance of grassroots innovation and community involvement in environmental conservation. By empowering local actors and providing them with the tools they need, these initiatives aim to create a ripple effect that can lead to significant environmental improvements at both local and global levels.
In conclusion, these new efforts reflect a growing recognition of the interconnectedness of technology, ecosystems, and economies. As we move forward, it is essential to continue fostering collaborations that bridge these domains, ensuring that our collective actions lead to a sustainable and resilient future for all. For further details on these initiatives, interested parties are encouraged to visit the original sources for comprehensive information.
For more Information, Refer to this article.