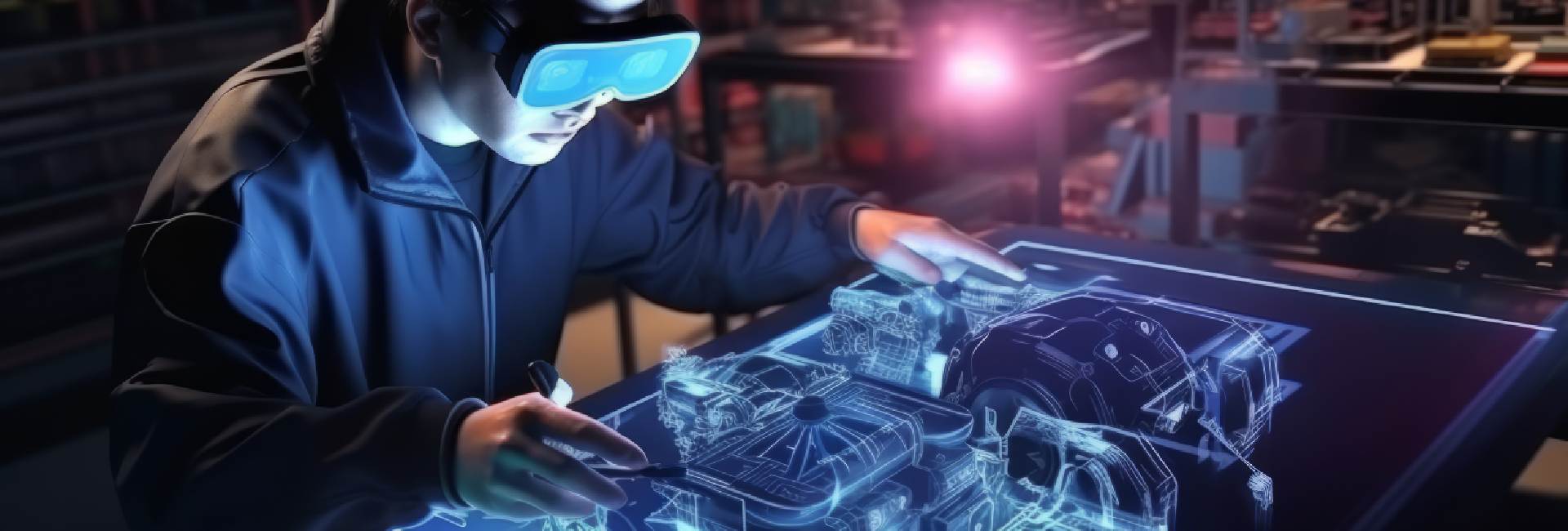
The manufacturing industry is continuously evolving, driven by the need for constant improvement and adaptation. One of the most significant advancements in recent years is the integration of Virtual Reality (VR) into industrial training and manufacturing processes. VR offers a transformative approach to traditional manufacturing, providing immersive experiences that redefine how manufacturers approach design, production, and workforce development. In this post, we delve into how VR is revolutionizing the manufacturing sector and explore the benefits it brings to the table.
Reimagining Product Design and Development
In the past, developing new products required creating multiple physical prototypes, which involved substantial material costs and manual labor. This method was not only expensive but also time-consuming. Today, VR technology has transformed this process by enabling manufacturers to create detailed virtual prototypes that can be tested and refined rapidly without any physical constraints.
Industry giants like Ford and Boeing have embraced VR prototyping, leading to significant improvements in their design cycles. By utilizing immersive 3D environments, engineers can interact with complex designs in real-time, reducing the time required for prototype development by up to 60%. This approach eliminates material waste, minimizes production delays, and cuts down on development costs.
Virtual testing represents a major leap forward in product development. Engineers can now subject virtual prototypes to various stressors such as temperature changes, pressure, and wear and tear. This capability has resulted in a 75% reduction in the need for physical testing in industries like aerospace and automotive, thanks to advanced VR simulation technologies.
These virtual environments allow engineers to observe material stress, mechanical interactions, and performance parameters in great detail. They can predict potential failure points and optimize designs before manufacturing any physical components, ensuring that products meet industry standards and perform reliably in real-world conditions without needing physical testing environments.
Furthermore, VR technology has overcome geographic barriers that previously hindered collaborative design processes. It provides shared digital workspaces where global teams can interact with design models simultaneously, irrespective of their physical locations. For instance, a design engineer in Detroit can collaborate in real-time with colleagues in Tokyo, manipulating 3D models, discussing modifications, and making instant adjustments. This global collaboration accelerates decision-making, reduces communication delays, and ensures consistent design quality across international teams.
Enhancing Factory Workflows
VR technology allows manufacturers to simulate entire production lines and workflows, creating digital twins of production environments. This capability enables them to identify inefficiencies, bottlenecks, or potential failure points before making physical changes. Companies like Toyota have utilized VR simulations to redesign factory layouts, achieving up to a 30% improvement in production line efficiency. This digital transformation empowers managers to experiment with different configurations, test workflow scenarios, and make data-driven decisions without risking actual production interruptions.
Traditional factory floor planning relied on 2D blueprints and physical measurements. VR changes this approach by offering immersive, interactive spatial planning tools. Managers can walk through virtual factory layouts, assess equipment interactions, analyze worker movement patterns, and test configurations for equipment placement, workflow paths, and storage solutions. Optimizing these elements virtually leads to better space utilization and enhanced productivity.
Training the Workforce of the Future
Manufacturing training has traditionally been high-risk, expensive, and inconsistent. VR-based training solutions address these challenges by providing safe, repeatable learning environments. Employees can practice complex machinery operations, learn complicated procedures, and develop muscle memory without endangering themselves or risking equipment damage.
Research indicates that VR training can decrease learning time by 40% while increasing knowledge retention by 75%. These are not just marginal improvements; they represent a fundamental transformation in workforce skill development.
Safety is a critical concern in manufacturing environments. VR-based training solutions allow employees to experience and respond to hazardous scenarios in controlled, risk-free environments. From handling chemical spills to executing emergency equipment shutdowns, workers can develop critical safety skills without exposing themselves to actual risks.
Cost Savings Through Smart Processes
VR technologies offer substantial economic benefits by reducing physical prototyping costs, minimizing training expenses, and optimizing workflow efficiencies. For example, Boeing’s use of VR smart glasses in wiring assembly reduced assembly times by 25%, highlighting the financial advantages of integrating virtual tools into manufacturing processes.
In conclusion, VR is not just about improving efficiency in manufacturing; it is about redefining the entire approach to design, production, and workforce development. As more companies adopt VR technologies, the manufacturing industry is poised for significant advancements, leading to more innovative products, efficient processes, and a more skilled workforce. This transformation is not just futuristic—it is happening now, reshaping the landscape of manufacturing for years to come.
For those interested in exploring further, additional insights and case studies on VR applications in manufacturing can be found at Juegos Studio.
For more Information, Refer to this article.