Google’s New Trillium TPU: A Leap in AI Processing Power
Earlier this year, during the I/O event in May, Google unveiled its latest advancement in AI technology: the Trillium, the sixth iteration of its custom-designed chip, the Tensor Processing Unit (TPU). Recently, Google made a significant announcement revealing that Trillium is now available for Google Cloud customers in a preview phase. This development marks a substantial leap in processing power and sustainability for AI applications.
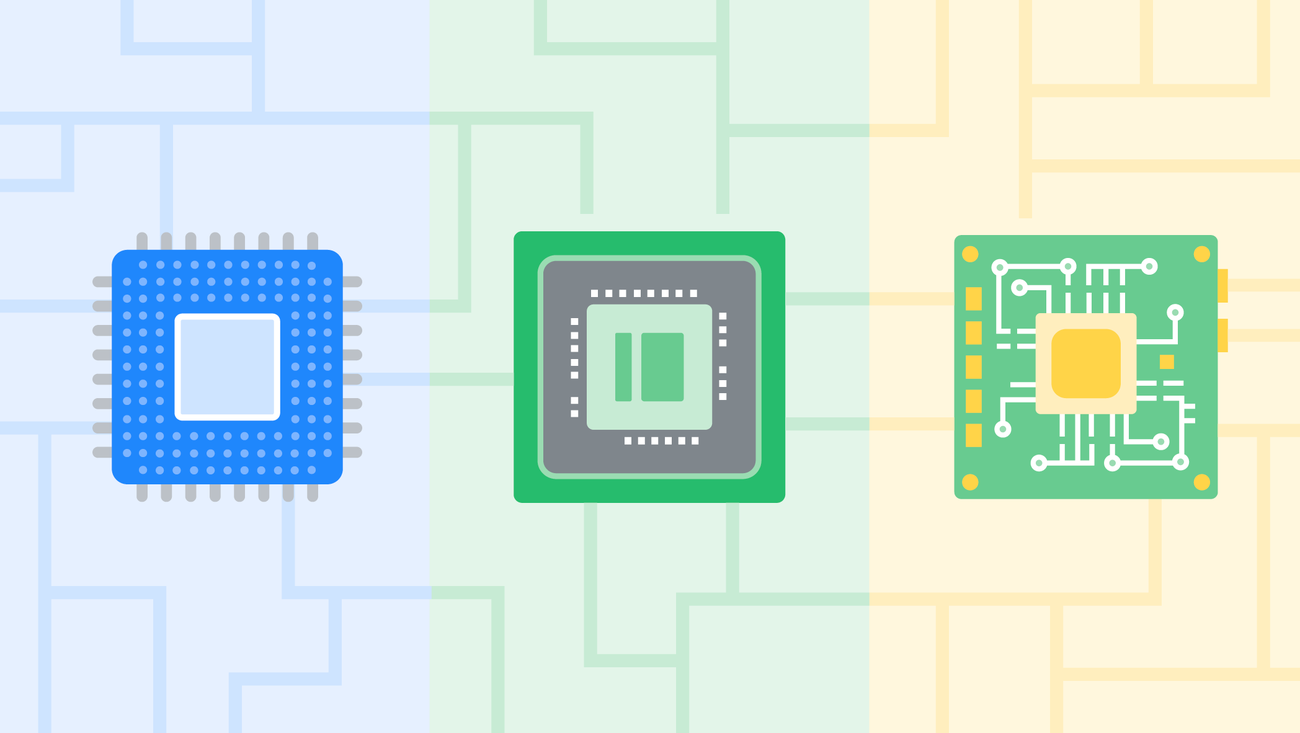
But what exactly is a TPU, and what sets Trillium apart from its predecessors? To delve into the specifics, it’s crucial to understand the different types of processors available, namely CPUs, GPUs, and TPUs, and how they differ from one another. Chelsie Czop, a product manager at Google Cloud specializing in AI infrastructure, offers insights into these components. “I collaborate with various teams to ensure our platforms deliver maximum efficiency for customers developing AI products,” she explains. One of the critical components enabling Google’s AI innovations is, indeed, Google’s TPUs.
Understanding Processors: CPUs, GPUs, and TPUs
Processors, the brains behind compute tasks, can be likened to a human brain performing activities such as reading or solving math problems. These tasks are analogous to compute tasks your device performs when you take a picture, send a text, or open an application. Here’s a breakdown of the different types of processors:
Central Processing Unit (CPU):
The CPU is a general-purpose chip capable of handling a wide range of tasks. While it can manage various functions, it may take longer for tasks outside its specialization, similar to a human brain tackling unfamiliar problems.
Graphics Processing Unit (GPU):
GPUs are the powerhouses for accelerated compute tasks, handling everything from rendering graphics to processing AI workloads. They belong to a category known as ASICs, or application-specific integrated circuits. These circuits are typically made from silicon, which is why chips are often referred to as "silicon." This is also the origin of the term “Silicon Valley.” ASICs are crafted for specific purposes, making them highly efficient in their designated roles.
Tensor Processing Unit (TPU):
Google’s TPUs are its proprietary ASICs, engineered specifically for AI-based compute tasks. They are more specialized than both CPUs and GPUs and have been integral to many of Google’s AI services, including Search, YouTube, and DeepMind’s advanced language models.
The Role of Processors in Everyday Devices and Data Centers
CPUs and GPUs are ubiquitous in everyday devices. CPUs are found in almost every smartphone and personal computing device like laptops. GPUs, on the other hand, are common in high-end gaming systems and some desktop computers. TPUs, however, are exclusive to Google data centers. These facilities, resembling warehouses, are filled with rows of TPUs working continuously to support Google’s and Google Cloud customers’ AI services globally.
The Genesis of Google’s TPU Innovation
The journey toward developing TPUs began about a decade ago at Google. With the rapid improvement in speech recognition services, Google realized it would need to double its data center computing power if users began interacting with Google for just three minutes daily. Recognizing the inefficiency of existing hardware, Google embarked on creating a new, more efficient processing solution, resulting in the birth of the TPU.
Why "Tensor" in Tensor Processing Unit?
In the context of machine learning, a "tensor" is a fundamental data structure. Underneath the surface, complex mathematical operations are essential for AI tasks. With Trillium, the latest TPU, Google has significantly increased the computational capabilities. Trillium boasts 4.7 times the peak compute performance per chip compared to its predecessor, the TPU v5e.
What Does Enhanced Performance Mean for Trillium?
The improved performance of Trillium translates into its ability to execute complex calculations 4.7 times faster than the previous generation. Besides being faster, Trillium can also manage larger and more intricate workloads, making it a formidable tool in AI processing.
Trillium’s Advances in Energy Efficiency
Trillium is not only more powerful but also Google’s most sustainable TPU to date. It offers a 67% improvement in energy efficiency compared to its predecessor. As AI demand escalates, it is crucial to scale infrastructure sustainably. Trillium achieves the same computational tasks while consuming significantly less power, aligning with environmental sustainability goals.
The Anticipated Impact of Trillium
The initial feedback from Trillium users is already showcasing incredible advancements. Customers are leveraging Trillium in technologies that analyze RNA for disease research, convert written text into videos at unprecedented speeds, and more. These examples represent just the beginning—now that Trillium is available in preview, the potential applications are boundless.
In conclusion, the introduction of Trillium marks a significant milestone in AI technology, promising enhanced performance and sustainability. As Google Cloud customers begin to explore the capabilities of this new TPU, the world can anticipate groundbreaking innovations in AI-driven solutions.
For more Information, Refer to this article.