Pioneering Health Monitoring: From Space Technology to Heart Failure Management on Earth
Health maintenance is crucial for everyone on Earth and becomes even more vital for astronauts venturing into space. Space exploration subjects humans to unique environments that can significantly impact various aspects of health, including blood pressure, bone density, and immune function. Recognizing these challenges, two NASA inventors embarked on a mission two decades ago to develop a technology capable of monitoring astronaut heart health during extended space missions. This groundbreaking technology is now being adapted for patients suffering from heart failure on Earth, with its commercial launch anticipated in late 2024.
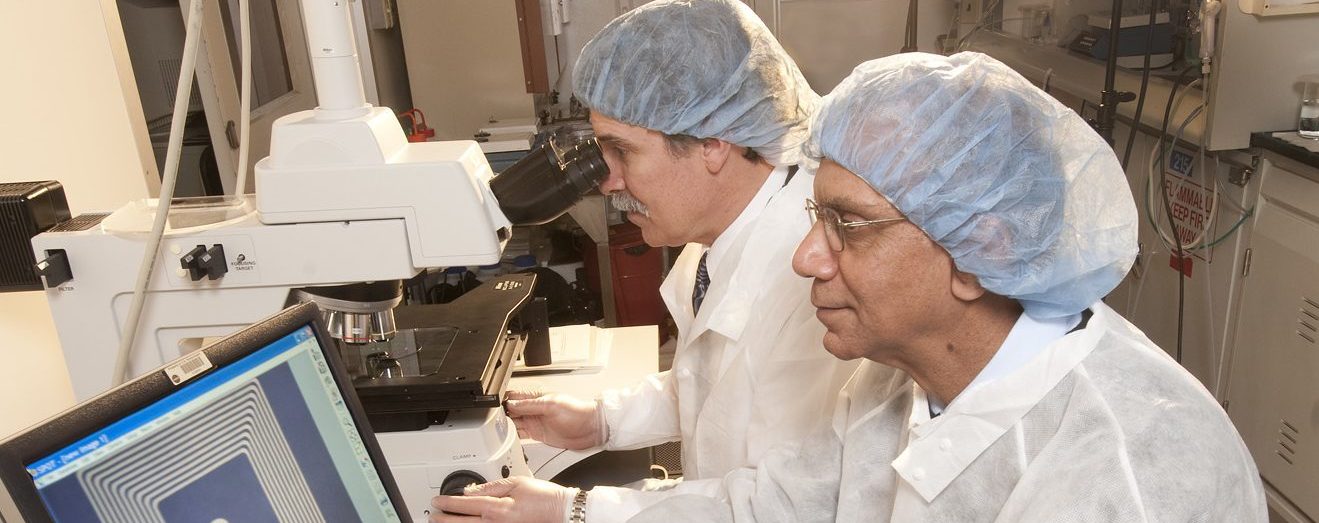
NASA’s innovative minds, Dr. Rainee Simons, a senior microwave communications engineer, and Dr. Félix Miranda, the deputy chief of the Communications and Intelligent Systems Division, combined their expertise in radio frequency integrated circuits and antennas to create a revolutionary health-monitoring sensor. Developed at NASA’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland, with initial funding from the agency’s Technology Transfer Office, this miniature implantable sensor system was designed to track astronaut health in space. The sensor is remarkable for being both battery-less and wireless, capable of transmitting health data from the body directly to a handheld device.
"You can insert the sensor and position it near the heart or the aorta, similar to how a stent is placed," explained Dr. Simons. "This process does not require major surgery, and the external handheld device is user-friendly for patients."
Upon securing a patent for this invention, Dr. Anthony Nunez, a heart surgeon, and Harry Rowland, a mechanical engineer, saw its potential beyond space applications. In 2007, they licensed the technology and founded a digital health company called Endotronix, now part of Edwards Lifesciences. Endotronix is committed to proactive heart failure management through data-driven solutions that bridge patient-to-physician communications, utilizing the foundational technology developed at Glenn.
The centerpiece of Endotronix’s offerings is the Cordella Pulmonary Artery (PA) Sensor System. Dr. Nunez discovered this technology while perusing a technical journal and envisioned its transformative potential in medical applications. This innovative concept has demonstrated substantial benefits for heart failure management across multiple clinical trials, leading to notable improvements in patients’ quality of life. Following rigorous clinical testing to ensure its safety and efficacy, the Cordella PA Sensor System received premarket approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in June 2024. The system enables healthcare providers to remotely monitor, assess, and manage heart failure in patients from the comfort of their homes, thereby aiming to reduce hospital admissions.
"If you consider the number of people affected by congestive heart failure and high blood pressure, it’s staggering," Dr. Miranda noted. "Having a medical device born from NASA’s intellectual property that has the potential to aid people globally in leading healthier, more fulfilling lives aligns perfectly with NASA’s mission to benefit humanity."
Understanding the Technology
To appreciate the significance of this innovation, it is essential to understand some of the technical aspects involved. The sensor operates without a battery, drawing power from external sources, which makes it highly efficient and reduces the need for frequent maintenance or replacements. The wireless communication capability allows seamless transmission of health data, which is crucial for real-time monitoring, especially in remote or challenging environments like space, or for patients who may not be able to visit a healthcare facility frequently.
The process of inserting the sensor is minimally invasive, akin to a stent implant, which involves threading the sensor through blood vessels to its destination near the heart. This method considerably reduces the risks and recovery time associated with traditional surgeries, making it a safer option for patients with existing health conditions.
The Broader Impact and Future Prospects
The adaptation of space technology for terrestrial medical applications underscores the broader impact that space exploration can have on our daily lives. By addressing the unique challenges faced by astronauts, NASA’s innovations often lead to breakthroughs that benefit society at large. The transition of this heart-monitoring technology from space missions to healthcare settings exemplifies this phenomenon.
Moreover, the success of the Cordella PA Sensor System highlights the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in advancing medical technology. The partnership between NASA’s engineers and medical professionals at Endotronix demonstrates how combining expertise from different fields can lead to groundbreaking solutions that tackle pressing health challenges.
Reactions and Reviews
The medical community has responded positively to the introduction of the Cordella PA Sensor System. Clinicians appreciate its potential to enhance patient care by enabling continuous monitoring and timely interventions, which are critical in managing chronic conditions like heart failure. Patients, too, have expressed satisfaction with the system, noting improvements in their ability to manage their condition and maintain a better quality of life.
The approval of this technology by the FDA further validates its safety and efficacy, bolstering confidence among healthcare providers and patients alike. As it becomes more widely available, it is expected to play a significant role in reducing the burden of heart disease, which remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide.
Good to Know
For those interested in the technical and practical aspects of such innovations, it’s noteworthy that the process of technology transfer, as illustrated by this example, is a vital mechanism through which scientific advancements reach the public. NASA’s Technology Transfer Program actively seeks to bring space-derived technologies to market, fostering partnerships that enhance both economic growth and public welfare.
In conclusion, the journey of this sensor technology from space to Earth is a testament to the ingenuity and vision of scientists and engineers dedicated to improving human health. As this technology is integrated into mainstream healthcare, it promises to transform how heart failure is managed, providing a beacon of hope for millions of patients worldwide. For more information on the original concept, you can refer to NASA’s Glenn Research Center website.
For more Information, Refer to this article.