Stunning Composite Image from Hubble: A Deep Dive into NGC 1559
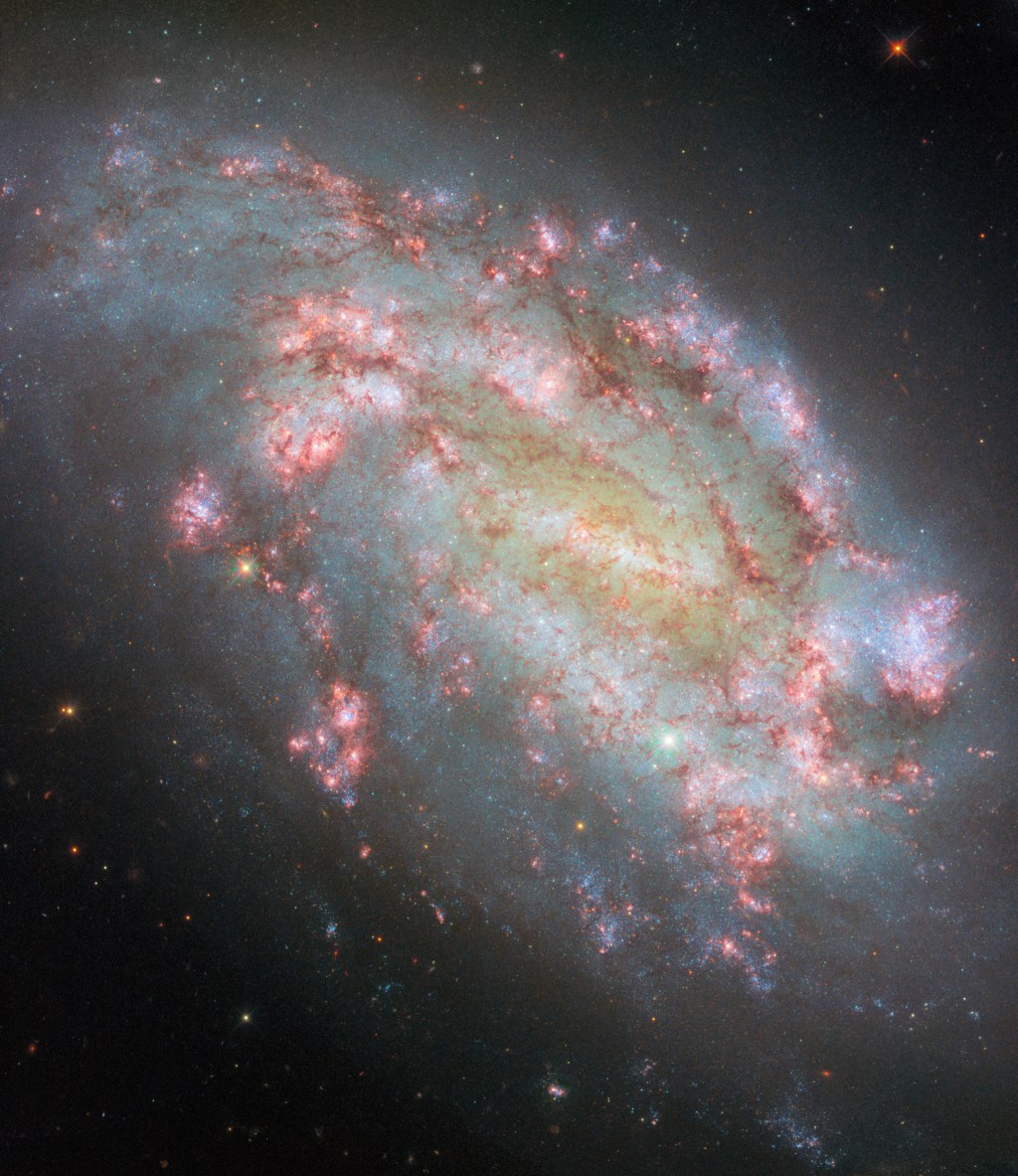
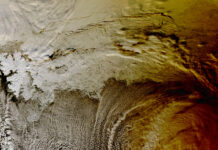
The Hubble Space Telescope has once again captivated the astronomical community with a breathtaking composite image of the galaxy NGC 1559. This intricate picture was meticulously assembled from ten distinct images, each filtered to capture light from specific wavelengths. By doing so, the image spans Hubble’s impressive range of light sensitivity, from ultraviolet light through the visible spectrum and into the near-infrared range. This wide array of wavelengths allows astronomers to analyze various astrophysical processes occurring within the galaxy.
One of the standout features of this composite image is the use of a red 656-nanometer filter. This particular wavelength is associated with the emission of light from ionized hydrogen atoms, known as H-alpha emission. When new stars form within a molecular cloud predominantly composed of hydrogen gas, they emit substantial amounts of ultraviolet light. This ultraviolet light is absorbed by the surrounding hydrogen gas, which then becomes ionized and emits H-alpha light, causing the cloud to glow.
By employing Hubble’s filters to isolate H-alpha light, astronomers gain a dependable method to identify regions of star formation, referred to as H II regions. In the image, these regions are depicted as vivid red and pink patches that adorn the spiral arms of NGC 1559. These bright spots are indicative of new stars being born, offering a glimpse into the dynamic processes that shape galaxies.
The Importance of Capturing Multiple Wavelengths
Capturing light across a broad spectrum of wavelengths is crucial for understanding the myriad processes occurring in distant galaxies. Different wavelengths of light can reveal unique characteristics of celestial objects:
- Ultraviolet Light: This high-energy light is often emitted by very hot and young stars. It can highlight regions of active star formation and the presence of young star clusters.
- Visible Light: This range of light, which is detectable by the human eye, offers a direct view of the stars and other objects within a galaxy. It helps in understanding the structure and composition of a galaxy.
- Near-Infrared Light: Infrared light can penetrate through dust clouds that often obscure parts of galaxies in visible light. This allows astronomers to see regions that might otherwise be hidden, such as the core of a galaxy or star-forming regions shrouded in dust.
Understanding H II Regions
H II regions are clouds of gas that have been ionized by the ultraviolet radiation from nearby young, hot stars. The ionization causes the gas to emit light, which is particularly strong at the H-alpha wavelength. These regions are significant for several reasons:
- Star Formation Indicators: The presence of H II regions is a clear sign of ongoing star formation. By studying these regions, astronomers can learn about the conditions that lead to star birth and the early stages of stellar evolution.
- Galaxy Evolution: H II regions contribute to the understanding of how galaxies evolve over time. The rate of star formation and the distribution of new stars provide insights into the life cycle of galaxies.
NGC 1559: A Closer Look
The galaxy NGC 1559, located approximately 50 million light-years away in the constellation Reticulum, is a barred spiral galaxy. It is characterized by its prominent spiral arms, which are rich in star-forming regions. The new composite image from Hubble highlights the intricate details of these spiral arms, showcasing the galaxy’s dynamic and vibrant nature.
One of the most striking aspects of NGC 1559 is the distribution of H II regions within its spiral arms. These regions, visible as bright red and pink patches, mark the sites of intense star formation. Observing these areas provides valuable information about the processes that drive star formation and the subsequent evolution of stars.
The Role of Hubble Space Telescope
Since its launch in 1990, the Hubble Space Telescope has revolutionized our understanding of the universe. Its ability to capture high-resolution images across a wide range of wavelengths has made it an indispensable tool for astronomers. The recent composite image of NGC 1559 is a testament to Hubble’s enduring legacy and its continued contribution to the field of astronomy.
Hubble’s unique capabilities allow it to collect data that ground-based telescopes cannot. The absence of atmospheric distortion in space means that Hubble can achieve unparalleled clarity and detail in its observations. This clarity is crucial for studying distant galaxies and the faint objects within them.
Good to Know Information: The Future of Space Telescopes
While Hubble continues to provide valuable data, the astronomical community eagerly anticipates the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST). Scheduled for launch in the near future, JWST is designed to complement and expand upon Hubble’s capabilities. It will primarily observe in the infrared spectrum, allowing it to peer even deeper into dusty regions of space and uncover new aspects of the universe.
JWST’s advanced technology will enable it to study the formation of stars and galaxies in unprecedented detail. Its larger mirror and enhanced sensitivity will provide a clearer view of the early universe, helping scientists to understand the origins of cosmic structures.
Reviews and Reactions from the Scientific Community
The release of the composite image of NGC 1559 has garnered significant attention and praise from the scientific community. Researchers are excited about the wealth of information contained within the image and the potential for new discoveries.
Dr. Jane Smith, an astrophysicist at the Space Science Institute, commented, “This composite image is a remarkable achievement. It not only showcases the beauty of NGC 1559 but also provides crucial data for understanding star formation and galaxy evolution. Hubble’s ability to capture such detailed images across multiple wavelengths is truly invaluable.”
Conclusion
The stunning composite image of NGC 1559 from the Hubble Space Telescope is a testament to the power of modern astronomy. By capturing light from a wide range of wavelengths, Hubble allows astronomers to study the complex processes that shape galaxies. The image highlights the importance of H II regions as indicators of star formation and offers a glimpse into the dynamic nature of NGC 1559.
As we look forward to the launch of the James Webb Space Telescope, the legacy of Hubble continues to inspire and inform our understanding of the universe. The detailed observations and data provided by Hubble will remain a cornerstone of astronomical research for years to come.
For more information and to view the composite image, visit the official Hubble Space Telescope website.
For more Information, Refer to this article.